Session 03 - Introduction to CSS
Harvard Extension School
Fall 2024
Course Web Site: https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/
Topics
- CSS Mechanics - rules and selectors
- Basic Selectors - elements, class, id
- CSS Properties and Values
- Starting off with CSS
- Working an Example
- Box Model or Block Model
- Colors
- Backgrounds
- Hypertext Links
- Fonts
Presentation contains 48 slides
Client-side Web Parts: Structure, Style, Function
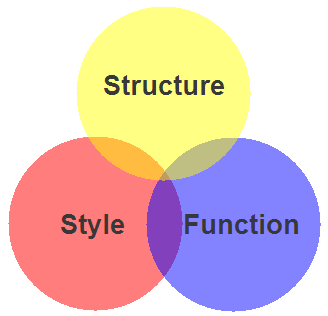
- Structure / Markup (HTML)
- Structure
- Content
- Style / Presentation (CSS)
- Style
- Presentation
- Appearance
- Function (JavaScript)
- Actions
- Manipulations
Structure, Style, Function
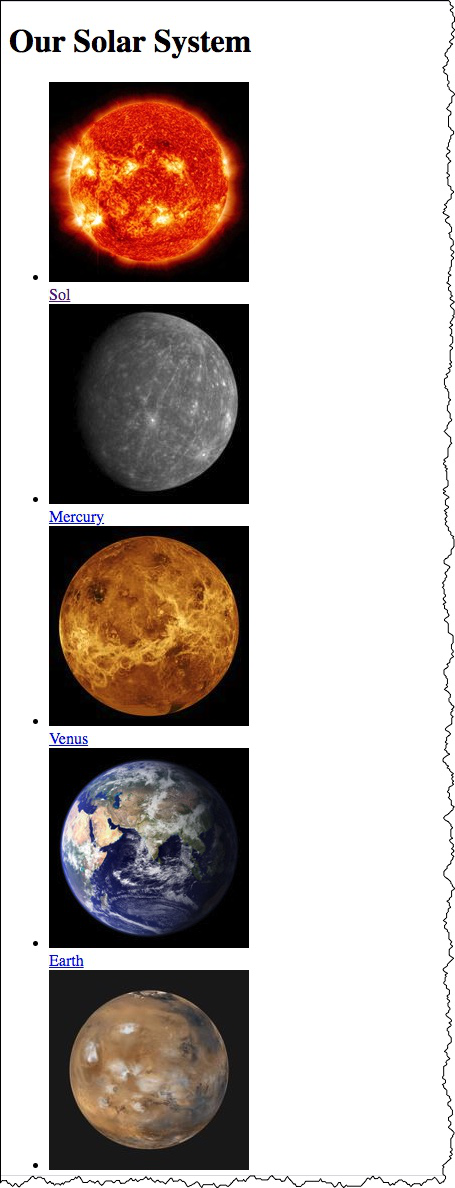

Styles
The markup page references an external stylesheet document.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Our Solar System</title>
<!-- the link element is used to reference a stylesheet -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles/solarsystem.css" />
The CSS file contains style rules for the document (solarsystem.css)
body {
margin-left: 5%;
margin-top: 2rem;
margin-right: 5%;
background-image: linear-gradient(#ffffff, #ffffef);
background-color: #ffffdd;
font-family: Calibri, Arial, sans-serif;
min-height: 100vh;
}
h1 {
font-family: Calibri, Arial, sans-serif;
color: #333333;
border-bottom: 3px solid #333333;
}
ul.gallery {
list-style: none;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
justify-content: flex-start;
}
ul.gallery li {
font-size: 1.25rem;
flex-basis: 1 0 auto;
text-align: center;
border: thin dotted #333333;
margin: 0.8rem;
padding: 0.8rem;
}
ul.gallery li img {
border: none;
}
footer {
margin-top: 2rem;
padding: 1rem;
font-size: smaller;
}
a:link, a:visited {
text-decoration: none;
color: blue;
}
a:hover {
text-decoration: underline;
}
a:active {
border: none;
text-decoration: none;
}Different Styles for The United States Constitution
- Chocolate Stylesheet
- Midnight Stylesheet
- Modernist Stylesheet
- Oldstyle Stylesheet
- Steely Stylesheet
- Swiss Stylesheet
- Traditional Stylesheet
- Ultramarine Stylesheet








University of Colorado - Boulder
CU Boulder - Home  | With CSS disabled:  |
Responsive Web Design
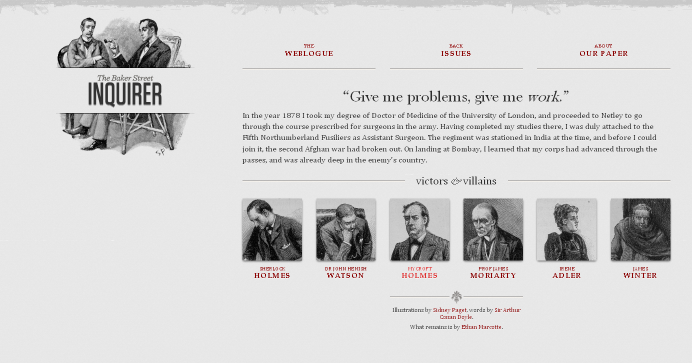


CSS Guides and Reference
- CSS: Cascading Style Sheets | MDN
- CSS reference | MDN
CSS Validator
CSS Specifications (likely not too useful)
- CSS Current Work (CSS level 3)
CSS Mechanics - rules and selectors
- Rules
- Selectors
Anatomy of a CSS Rule
CSS Rule

Selector and Declarations

Properties and Values
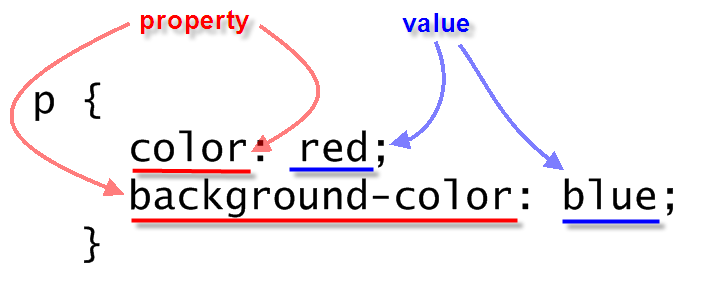
Simple CSS Example
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</p> In style
element
(<style>) within head element:
p {
color: red;
background-color: blue;
}
CSS Mechanics - Binding Styles to Markup
Three ways to bind CSS rules to HTML markup:
styleattribute in element<style>element in HTML head- External CSS document, through the
<link>element in HTML head
style attribute
<p style="color: black; background-color: teal; padding: 1em; font-family: helvetica, sans-serif; text-align: justify; margin: 2rem;">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</p>
style element
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</p> In style
element
(<style>) within head element:
p {
color: black;
background-color: teal;
padding: 1em;
font-family: helvetica, sans-serif;
text-align: justify;
margin: 2rem;
}
So the full page looks like:
<html>
<head>
<title>CSCIE-12 CSS Example</title>
<style>
p {
color: black;
background-color: teal;
padding: 1em;
font-family: helvetica, sans-serif;
text-align: justify;
margin: 2rem;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec
facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit.
Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante
sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</p>
</body>
</html>link element
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</p>In
head element:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="example4.css"/>In example4.css
p {
color: black;
background-color: teal;
padding: 1em;
font-family: helvetica, sans-serif;
text-align: justify;
margin: 2rem;
}

The full source:
<html>
<head>
<title>CSCIE-12 CSS Example</title>
<link href="example4.css" rel="stylesheet"/>
</head>
<body>
<p>
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec
facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit.
Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante
sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</p>
</body>
</html>Combining Rules
Rules can be combined so that a single declaration contains multiple rules. The following two sets of style rules would produce identical results.
Is this:
p {
color: black;
background-color: teal;
padding: 1em;
margin: 1em;
font-family: helvetica, sans-serif;
text-align: justify;
}Better than this?:
p {color: black;}
p {background-color: teal;}
p {padding: 1em;}
p {margin: 1em;}
p {font-family: helvetica, sans-serif;}
p {text-align: justify;}Combining Selectors
Is this:
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6 { color: maroon;}Better than this?:
h1 { color: maroon; }
h2 { color: maroon; }
h3 { color: maroon; }
h4 { color: maroon; }
h5 { color: maroon; }
h6 { color: maroon; }Basic Selectors - elements, class, id
- element selectors
- class selectors
- id selectors
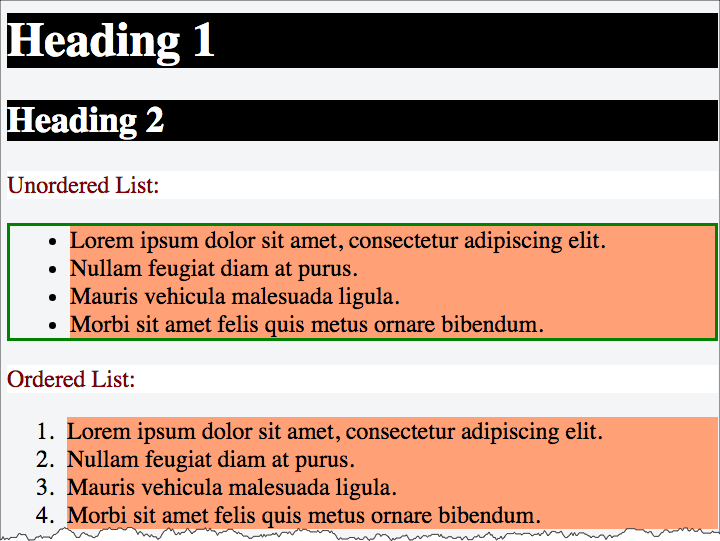
element selectors
p {
background-color: white;
color: maroon;
}
ul {
border: medium solid green;
}
li {
background-color: lightsalmon;
}
h1,
h2,
h3 {
background-color: black;
color: white;
}
class selectors
The class and id attributes of HTML elements can be used in conjunction with styles.
Class names are referenced in CSS as .classname, and may or may not have an element name preceding the period (.classname or element.classname.
Likewise, id names are referenced in CSS as #idref, where "idref" is the id name.
<div>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.
</div>
<div class="withstyle">Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</div>
<div class="warn">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.
</div>
<div>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,
<span class="warn">consectetuer adipiscing elit </span>. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.
</div>
<div id="terms-of-service">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.
</div> In style
element
(<style>) within head element:
div
{
background-color: white;
color: black;
font-family: times;
margin: 0.5em;
padding: 0.5em;
}
div.withstyle
{
background-color: #5c5c00;
color: white;
font-family: sans-serif;
margin: 0.5em;
padding: 0.5em;
}
.warn
{
border: 3px solid yellow;
color: #b30000;
font-weight: bold;
}
#terms-of-service
{
color: #575757;
font-size: 0.8em;
}id selectors
id names are referenced in CSS as #idref, and may or may not have an element name preceding the period (#idref or element#idref.
<header>
<h1>Lorem Ipsum </h1> </header>
<main><!-- main content -->
<section id="bigidea">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis. </section>
<section>Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. </section> </main>
<footer>Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis. </footer> In style
element
(<style>) within head element:
h1 { text-align: center; }
section { margin: 1rem; }
footer { margin: 1rem;
padding: 1rem;
border-top: thin solid black;
background-color: #f0f0f0;
}
#bigidea {
background-color: blue;
color: white;
border-color: green;
border-width: thick;
border-style: solid;
line-height: 1.5;
padding: 1rem;
} Contextual Selectors
selector1 selector2 { ...rules... }
Often you'll see this as ways to apply different rules in header,
main, and footer
main p {
/* rules for p inside of main */
}
footer p {
/* rules for p inside of main */
}
h2 {
/* rules for h2 */
foo
}
section h2 {
/* rules for h2 inside of section */
}
Example of "li em" selector
<div>
<em>Emphasized text </em>outside of
<strong>li </strong>appear with default styules.
<ul>
<li>
<em>Emphasized text </em>within
<strong>li </strong>have a different style.
</li> </ul>
</div> In style
element
(<style>) within head element:
li em { color: red; background-color: navy;}
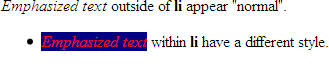
CSS Properties and Values
CSS Properties
CSS Level 1 lists 53 properties.
- Font Properites
- font-family
- font-style
- font-variant
- font-weight
- font-size
- font
- Color and Background Properties
- color
- background-color
- background-image
- background-repeat
- background-attachment
- background-position
- background
- Text Properties
- word-spacing
- letter-spacing
- text-decoration
- vertical-align
- text-transform
- text-align
- text-indent
- line-height
- Box Properties
- margin-top
- margin-right
- margin-bottom
- margin-left
- margin
- padding-top
- padding-right
- padding-bottom
- padding-left
- padding
- border-top-width
- border-right-width
- border-bottom-width
- border-left-width
- border-width
- border-color
- border-style
- border-top
- border-right
- border-bottom
- border-left
- border
- width
- height
- float
- clear
- display
- Classification Properties
- white-space
- list-style-type
- list-style-image
- list-style-position
- list-style
CSS Level 2.1 lists 115 properties.
- azimuth
- background
- background-attachment
- background-color
- background-image
- background-position
- background-repeat
- border
- border-bottom
- border-bottom-color
- border-bottom-style
- border-bottom-width
- border-collapse
- border-color
- border-left
- border-left-color
- border-left-style
- border-left-width
- border-right
- border-right-color
- border-right-style
- border-right-width
- border-spacing
- border-style
- border-top
- border-top-color
- border-top-style
- border-top-width
- border-width
- bottom
- caption-side
- clear
- clip
- color
- content
- counter-increment
- counter-reset
- cue
- cue-after
- cue-before
- cursor
- direction
- display
- elevation
- empty-cells
- float
- font
- font-family
- font-size
- font-style
- font-variant
- font-weight
- height
- left
- letter-spacing
- line-height
- list-style
- list-style-image
- list-style-position
- list-style-type
- margin
- margin-bottom
- margin-left
- margin-right
- margin-top
- max-height
- max-width
- min-height
- min-width
- orphans
- outline
- outline-color
- outline-style
- outline-width
- overflow
- padding
- padding-bottom
- padding-left
- padding-right
- padding-top
- page-break-after
- page-break-before
- page-break-inside
- pause
- pause-after
- pause-before
- pitch
- pitch-range
- play-during
- position
- quotes
- richness
- right
- speak
- speak-header
- speak-numeral
- speak-punctuation
- speech-rate
- stress
- table-layout
- text-align
- text-decoration
- text-indent
- text-transform
- top
- unicode-bidi
- vertical-align
- visibility
- voice-family
- volume
- white-space
- widows
- width
- word-spacing
- z-index
CSS Level 3 has several hundred properties.
See MDN CSS reference index of properties.
Inheritance
<div>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,
<em>consectetuer adipiscing elit </em>. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
<ul>
<li>Lorem
</li>
<li>Ipsum
</li>
<li>Dolor
</li> </ul>
</div>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</p>
<ul>
<li>Lorem
</li>
<li>Ipsum
</li>
<li>Dolor
</li> </ul> In style
element
(<style>) within head element:
body { color: navy; }
em { color: red; }
div { color: green; }

Rule Specificity
The more specific selector wins!
For now:
id > class > elements > element
More about this next week!
Browsers (User-Agents) have a default stylesheet
That's why lists are bulleted, paragraphs have space above, headings are big and bold, etc.
Starting off with CSS
- Block Model
- Margin
- Border
- Padding
- Colors
- Backgrounds - colors and images
- Hypertext Links
- Fonts
- Classes
Working an Example
Let's create something like this: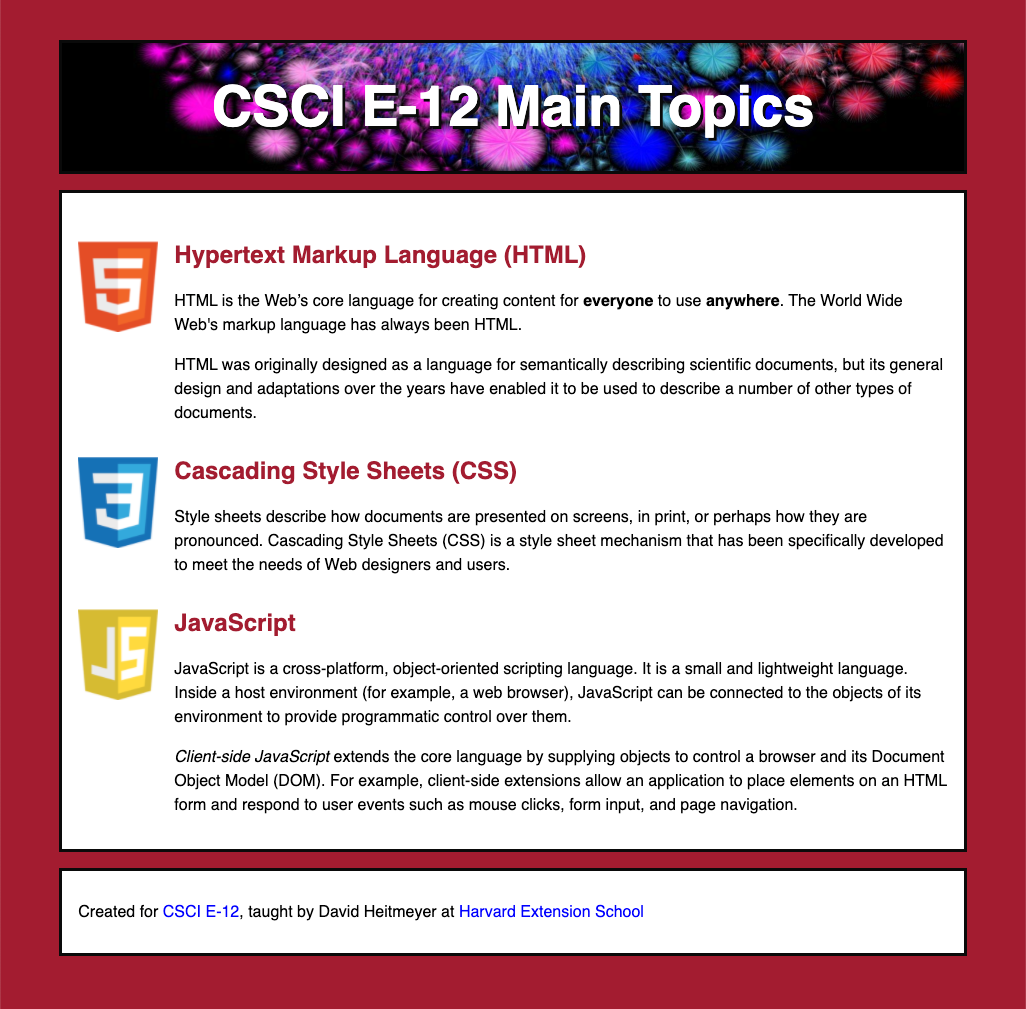
What do we see as the underlying markup?
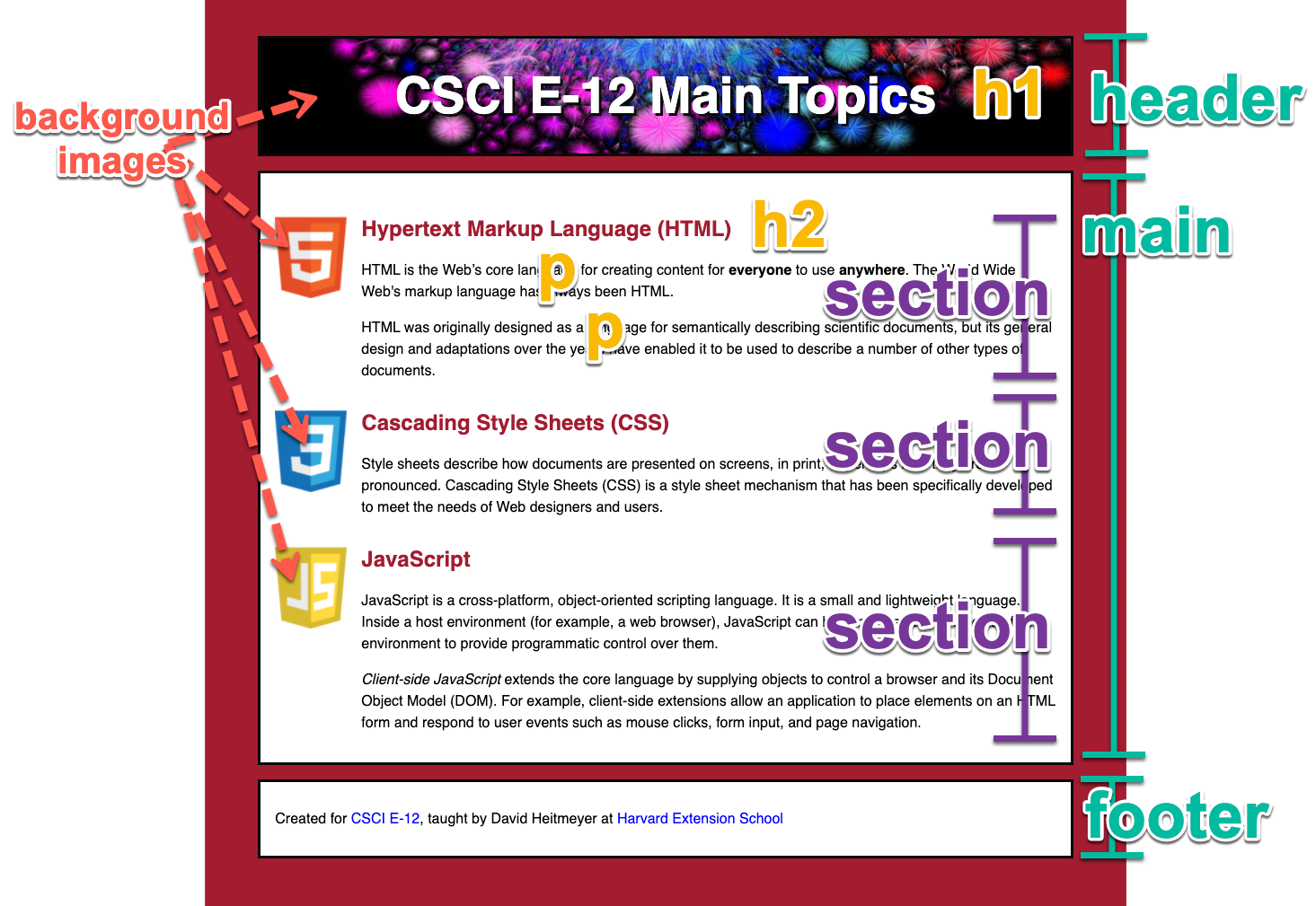
Here's some text to start us out
Files
├── images
│ ├── logo-css3.png
│ ├── logo-html5.png
│ ├── logo-js.png
│ └── opte-internet.jpg
├── index.html
├── reference_materials
│ ├── screenshot-main-topics-css-intro-annotated.png
│ ├── screenshot-main-topics-css-intro.png
│ └── text_content.txt
└── styles
└── site.cssText
Box Model or Block Model
- margin
- border
- padding
- content
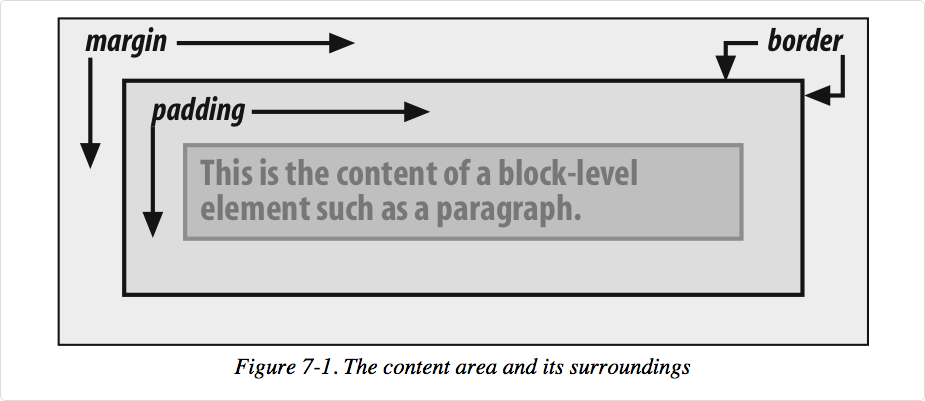
A more detailed look:
block-start, block-end, inline-start, inline-end
For LRTB writing, these correspond to top, bottom, left, and right.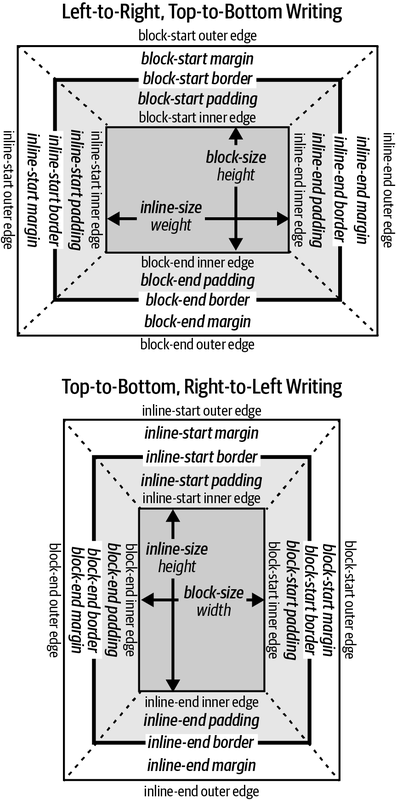
Think about the block axis (direction of multiple lines) and the inline axis (direction of line)
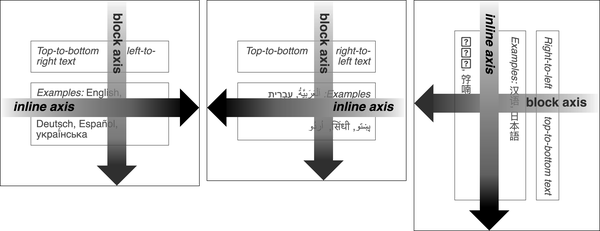
Image from CSS: The Definitive Guide, 5th ed by Eric Meyer and Estelle Weyl, published by O'Reilly
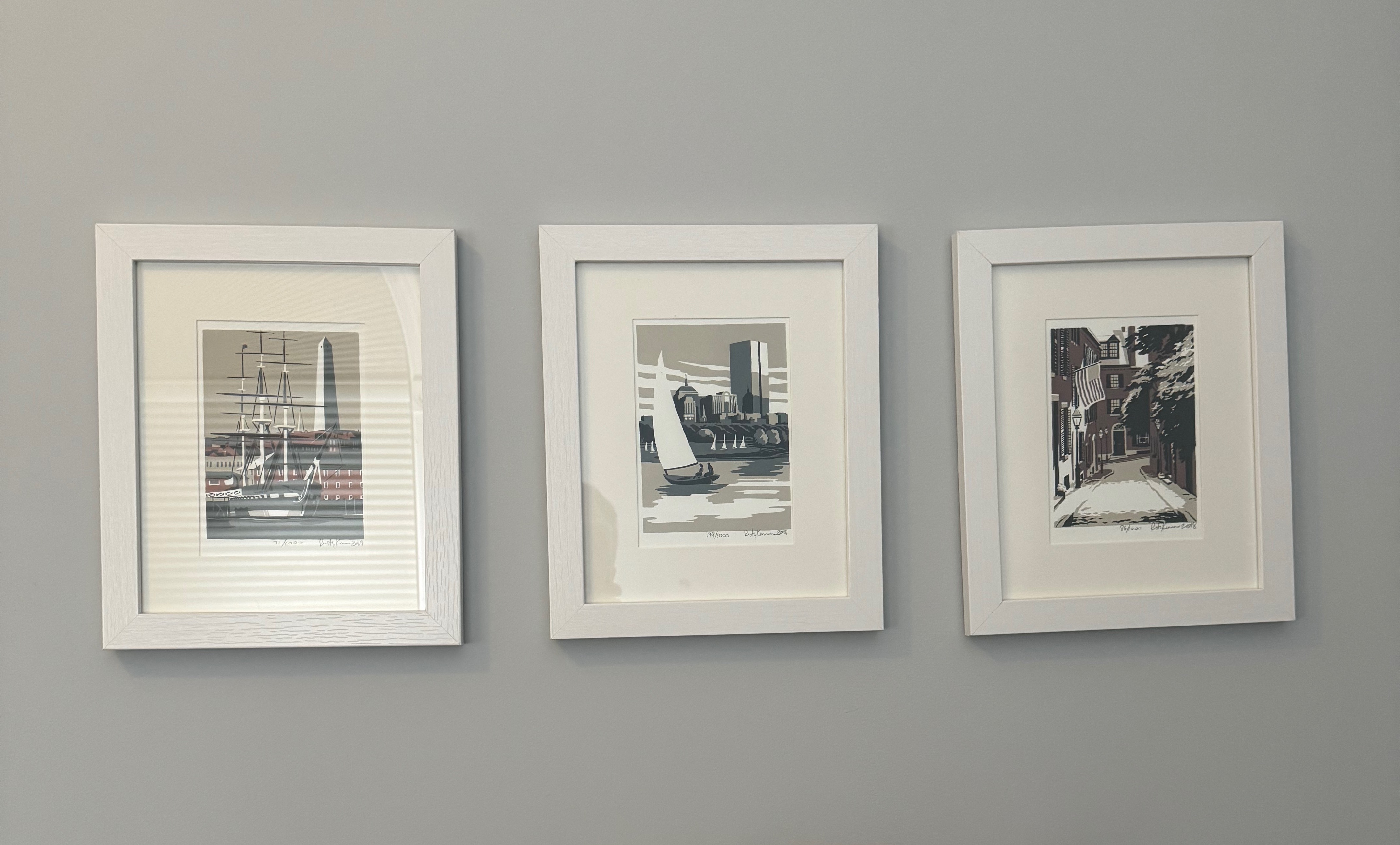
Frames on a Wall
Content = picture
Padding = matting
Frame = border
Margin = space between frames

Box Model revealed in your Browser
Use the "inspect" tool in your browser! Right click (or context click) and select "Inspect"
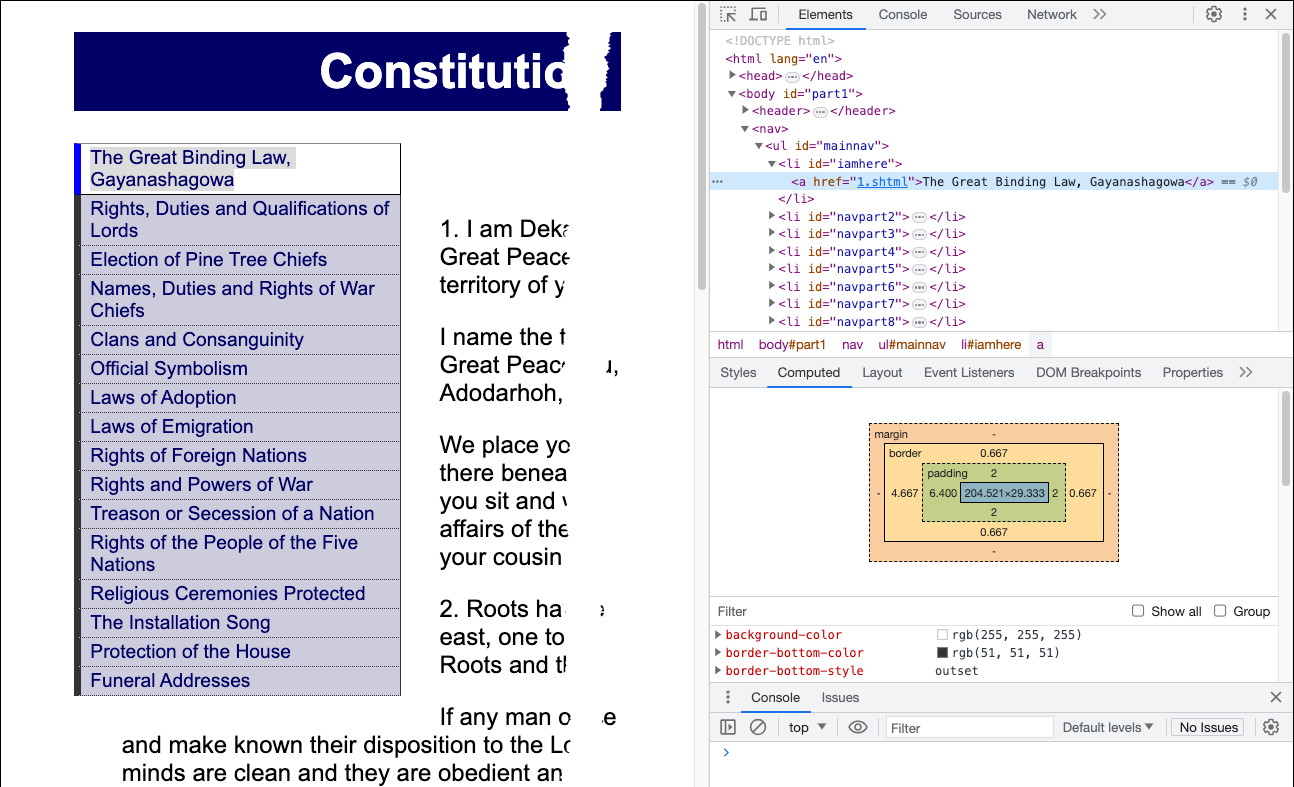
margin, padding, border
Properties are listed, with (equivalent properties for LRTB writing in parentheses)
- margin
- margin-block-start (margin-top)
- margin-block-end (margin-bottom)
- margin-inline-start (margin-left)
- margin-inline-end (margin-right)
- margin is shorthand property
- padding
- padding-block-start (padding-top)
- padding-block-end (padding-bottom)
- padding-inline-start (padding-left)
- padding-inline-end (padding-right)
- padding is shorthand property
- border
- border-block-start-width (you get the idea)
- border-block-end-width
- border-inline-start-width
- border-inline-end-width
- border-width is shorthand
- border-color
- border-style
- border-block-start (border-top) is shorthand
- border-block-end (border-bottom) is shorthand
- border-inline-start (border-left) is shorthand
- border-inline-end (border-right) is shorthand
- border is shorthand
border-style
<h4>Dotted </h4>
<p class="border1">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras feugiat mauris facilisis libero. Etiam nisl. Cras est dolor, viverra ac, ultrices volutpat, vestibulum et, odio. Nulla eget libero. Praesent eget tellus vel nibh nonummy egestas.
</p>
<h4>Dashed </h4>
<p class="border2">Etiam eu arcu quis lectus semper sodales. Donec vitae risus. Integer sollicitudin imperdiet dolor. Donec vehicula. Aliquam ut sapien sed eros imperdiet pharetra. Donec accumsan scelerisque leo. Sed eros nunc, pellentesque et, mollis non, faucibus venenatis, tortor.
</p>
<h4>Outset </h4>
<p class="border3">Pellentesque a velit. Sed pharetra vestibulum mauris. Ut vel arcu. Cras dolor ligula, eleifend et, ultrices nec, viverra in, ipsum. In convallis pharetra lacus. Etiam tellus. Aliquam quam. Vivamus mattis purus nec quam. Suspendisse hendrerit dui ac massa.
</p>
<h4>Solid </h4>
<p class="border4">Etiam rhoncus. Praesent id neque et odio dictum varius. Integer imperdiet blandit orci. Donec nec nunc posuere augue egestas accumsan. Nunc nonummy metus ut nunc. In id turpis vitae nisl eleifend bibendum. Curabitur cursus aliquam dolor.
</p>
<h4>Double </h4>
<p class="border5">Duis id erat a tortor laoreet aliquet. Quisque consectetuer lobortis mauris. Donec pede. Cras non turpis vel tortor iaculis nonummy. Ut facilisis viverra sem. Morbi pretium iaculis ligula. Praesent lectus. Aenean vel ante. Nunc interdum semper nisl. Pellentesque tincidunt.
</p>
<h4>Groove </h4>
<p class="border6">Aliquam leo nunc, congue a, imperdiet eget, aliquet ac, tortor. Sed ac est. Vivamus nisi. Mauris in nisl. Sed ultricies nunc vel nunc. In dignissim consequat arcu. Sed in risus. Nulla facilisi. Integer purus urna, laoreet vitae, congue a, posuere ut, ipsum. Nunc ac lacus sit amet nisi porttitor aliquam.
</p>
<h4>Ridge </h4>
<p class="border7">Vivamus dictum, sem in vulputate vestibulum, est tellus tempus dolor, ut laoreet arcu metus eu orci. Sed enim augue, dignissim sed, porta sed, dapibus ac, nibh. Nunc mattis ipsum eu lectus. Nam pharetra mattis massa.
</p>
<h4>Inset </h4>
<p class="border8">Maecenas consectetuer, lectus ac tempus iaculis, leo ipsum tincidunt erat, et aliquam libero nulla ac ipsum. Nam turpis leo, feugiat vel, nonummy id, ornare a, arcu. Vestibulum porta, justo et ornare porta, neque eros vestibulum libero, semper iaculis augue turpis eu neque.
</p> In style
element
(<style>) within head element:
body {
font-family: tahoma,arial,sans-serif;
font-size: small;
}
p {
margin: 1em;
padding: 1em;
width: 50%;
}
.border1 {
border: thin dotted #900;
}
.border2 {
border: medium dashed #090;
}
.border3 {
border: thick outset #009;
}
.border4 {
border: 3px solid #999;
}
.border5 {
border: 5px double #000;
}
.border6 {
border: 10px groove black;
}
.border7 {
border: 15px ridge black;
}
.border8 {
border: 20px inset #900;
}
TRBL for padding and margin shorthand
Stay out of "TRBL" (top right bottom left) for padding and margin shorthand.
But since we're trying to stay away from directions, mentally translate "top, right, bottom, left" to "block start, inline-end, block end, inline start"
Values that are present are used to fill in for values that are not:
padding: 1px 2px 3px 4px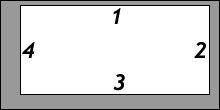
T = 1px; R = 2px; B = 3px; L = 4pxpadding: 1px 2px 3px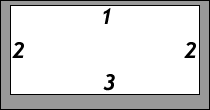
T = 1px; R = L = 2px; B = 3px;padding: 1px 2px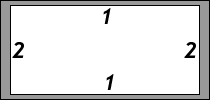
T = B = 1px; R = L = 2px;padding: 1px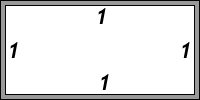
T = R = B = L = 1px
Colors
Color Names
As first defined in HTML: aqua, black, blue, fuchsia, gray, green, lime, maroon, navy, olive, purple, red, silver, teal, white, yellow
And then came 140 color names defined.
Color names OK for quick experiments, but we can do better.
RGB Color Space
- decimal numbers (0 to 255)
- hexadecimal numbers (00 to ff)
- percentages (0 to 100%)
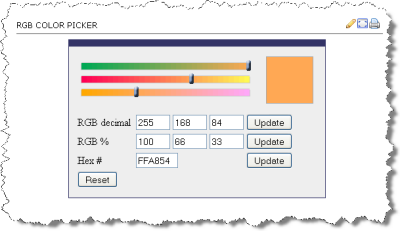
The following are all equivalent ways of defining a shade of orange:
|
<div style="background-color: rgb(100%,66%,33%); padding: 1em; ; margin: 1em;">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit.
<br/>
rgb(100%,66%,33%)
</div>
<div style="background-color: #ffa854; padding: 1em; margin: 1em; ">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit.
<br/>
#ffa854
</div>
<div style="background-color: rgb(255,168,84); padding: 1em; ; margin: 1em;">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit.
<br/>
rgb(255,168,84)
</div>Color and Palette Pickers
- Adobe Color
- Coolors Color Picker
- Simple Color Picker
- HTML HSL Color Picker from W3Schools
- ColorZilla - Browser Plugin to pick colors from web page
Backgrounds
- background-image
- background-repeat
- background-size
- background-position
See MDN Backgrounds and borders
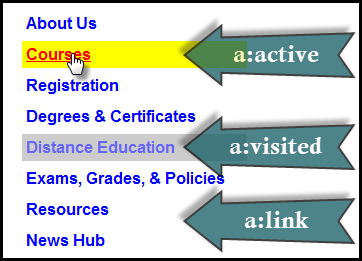
Hypertext Links
pseudo-classes for links (a elements)
- a:link
- a:visited
- a:hover
- a:active
Use the "link-visited-hover-active" or "LVHA" ordering (some like to remember this by "LoVe HAte").
<nav class="site">
<ul>
<li>
<a href="#about-us">About Us </a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#courses">Courses </a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#registration">Registration </a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#degrees-certificates">Degrees & Certificates </a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#distance-education">Distance Education </a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#exams-grades-policies">Exams, Grades, & Policies </a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#resources">Resources </a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#news-hub">News Hub </a>
</li> </ul> </nav> In style
element
(<style>) within head element:
nav a:link {
text-decoration: none;
color: blue;
background-color: white;
}
nav a:visited {
text-decoration: none;
color: #66f; /* lighter blue */
background-color: #ccc; /* grey */
}
nav a:hover {
text-decoration: none;
color: white;
background-color: blue;
}
nav a:active {
text-decoration: underline;
color: red;
background-color: yellow;
}
/**
Some tweaks to make the list
look more like a sidebar
navigation. Not important for
to illustrate the
a pseudo classes
*/
nav.site ul { font-family: sans-serif; font-weight: bold; width: 25%; list-style: none;}
a {margin: 0.25em; padding: 0.25em; display: block;}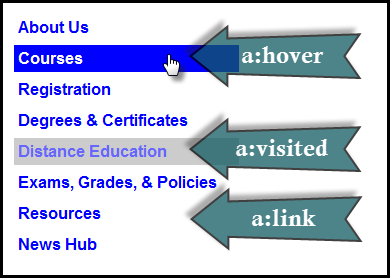

Fonts
- font-family
- font-style
- font-variant
- font-weight
- font-size
- font
font-family
body {
font-family: garamond, times, serif;
}
<div style="font-family: garamond, times, serif;">Garamond, Times, or serif (generic family)
</div>
<div style="font-family: calibri, arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">Calibri, Arial, Helvetica or sans-serif (generic family)
</div>
<div style="font-family: lucida console, courier, monospace;">Lucida Console, Courier or monospace (generic family)
</div>
<div style="font-family: fantasy;">Fantasy (generic family)
</div>
<div style="font-family: cursive;">Cursive (generic family)
</div>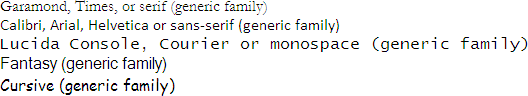
font-style
em {
font-style: italic;
}
<div style="font-style: normal;">Normal font-style
</div>
<div style="font-style: italic;">Italic font-style
</div>
<div style="font-style: oblique;">Oblique font-style
</div>font-variant and font-weight
font-variant
<div style="font-variant: small-caps;">This should be rendered in small-caps.
<div style="font-variant: normal;">Here we revert to "normal".
</div>
</div>font-weight
strong {
font-weight: bold;
}
<div>font-weight can be used to make
<span style="font-weight: bold">text appear bold </span>.
</div>font-size
em and rem units
rem is the em unit at the "root" level.
These are the preferred units! "em" and "rem"
Font-size examples
<div style="font-size: 8pt;">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.
</div>
<div style="font-size: 120%;">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.
</div>
<div style="font-size: 1.5em;">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.
</div>
<div style="font-size: 2rem;">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.
</div>Font Sizes: Relative vs. Absolute
As a general guideline with CSS, relative measurements are better than absolute measurements.
- Relative
- "rem" units
- Relative to UA settings:
xx-small | x-small | small | medium | large | x-large | xx-large rem- relative to the html "em" (root em)- Relative to context:
larger | smaller - Percentage (%)
- "em" units
- Absolute
- "pt" sizes (8pt, 10pt, 12pt)
"font" shorthand property
The font shorthand property allows you to set:[font-style | font-variant | font-weight ]? font-size[/line-height]? font-family
<div>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</div> In style
element
(<style>) within head element:
body {
font: normal normal normal x-large/200% arial, helvetica, sans-serif;
}
Web Fonts - Include through CSS link element
Using a link element to include CSS with @font-face definitions is how some font hosting services recommend including their fonts. Google Fonts does this.
The server delivering the fonts does browser detection and delivers the CSS file with the appropriate font format.
Note that we are having using two Google Fonts -- Cabin Sketch and Cabin. And we also link to our own stylesheet (demo.css).
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css2?family=Cabin+Sketch:wght@400;700&family=Cabin:wght@400;700&display=swap"
rel="stylesheet" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="demo.css" />Our CSS in demo.css:
h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6 {
font-family:"Cabin Sketch", sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 3rem;
}
h2 {
font-size: 2rem;
}
body {
font-family: sans-serif;
}
Note that nothing magical is going on here -- Google is simply returning CSS that uses @font-face with the font format appropriate for the browser making the request.
/* latin */
@font-face {
font-family: 'Cabin Sketch';
font-style: normal;
font-weight: 400;
font-display: swap;
src: local('Cabin Sketch Regular'), local('CabinSketch-Regular'), url(https://fonts.gstatic.com/s/cabinsketch/v14/QGYpz_kZZAGCONcK2A4bGOj8mNhNy_r-Kw.woff2) format('woff2');
unicode-range: U+0000-00FF, U+0131, U+0152-0153, U+02BB-02BC, U+02C6, U+02DA, U+02DC, U+2000-206F, U+2074, U+20AC, U+2122, U+2191, U+2193, U+2212, U+2215, U+FEFF, U+FFFD;
}
/* latin */
@font-face {
font-family: 'Cabin Sketch';
font-style: normal;
font-weight: 700;
font-display: swap;
src: local('Cabin Sketch Bold'), local('CabinSketch-Bold'), url(https://fonts.gstatic.com/s/cabinsketch/v14/QGY2z_kZZAGCONcK2A4bGOj0I_1Y5tjzAYOcFg.woff2) format('woff2');
unicode-range: U+0000-00FF, U+0131, U+0152-0153, U+02BB-02BC, U+02C6, U+02DA, U+02DC, U+2000-206F, U+2074, U+20AC, U+2122, U+2191, U+2193, U+2212, U+2215, U+FEFF, U+FFFD;
}Cheese and Wine Font Pairings
Font pairing — headings (h1,...,h6) and body
Try some professional advice on font pairing (a web search on "font pairing"
will get you started.)
Start with a font for headings and another font for body.
Font Resources
Finding or exploring fonts:
text properties
- word-spacing
- letter-spacing
- text-decoration
- vertical-align
- text-transform
- text-align
- text-indent
- line-height
Align blocks of text left, right, center, and justified.
<div style="margin-left: 30%; margin-right: 30%;">
<p style="text-align: left">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</p>
<p style="text-align: center">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</p>
<p style="text-align: right">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</p>
<p style="text-align: justify">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</p>
</div>
