Session 08 - Javascript, Part 1
Harvard Extension School
Fall 2023
Course Web Site: https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/
Topics
- JavaScript
- Getting Started with JavaScript
- JavaScript and HTML
- Document Object Model (DOM)
- JavaScript and Ice Cream
Presentation contains 22 slides
JavaScript
Goals for the JavaScript Unit- Understand where JavaScript fits into front-end web development
- Understand some basics in JavaScript
- Do essential operations:
- DOM manipulations
- if...else
- for..of loops
- objects
- events
- DOM
- JSON data structures
- Troubleshoot with browser console
- Do essential operations:
- Understand how to use JavaScript
- Separate JS from Markup
- Be able to incorporate JavaScript functionality into a site
- Be able to use JavaScript for commonly needed functionality
- Ready for more!
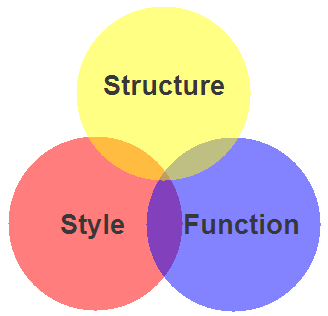
Client-side Web Parts: Markup, Style, Function
| Structure + Style + Function: solarsystem.html
Structure + Style: solarsystem-style.html
Structure: solarsystem-markup.html
|
Javascript
"JavaScript is now a language every developer should know."
– Mike Loukides, Vice President of Content Strategy for O'Reilly Media
JavaScript is everywhere:
- servers,
- rich web client libraries,
- HTML5,
- databases,
- even JavaScript-based languages.
Javascript
What is it?
- JavaScript is a programming language
- JavaScript runs within web browser
- Key concept in JavaScript is browser events
- But there's more — JavaScript can run on the server and command-line.
What can it do?
Javascript provides programmatic access to virtually all aspects of a page.
- CSS properties
- Markup content
- Forms, communication to Server
- Add functionality
ECMAScript and JavaScript
The standard for JavaScript is called ECMAScript.
Javascript Resources
- MDN JavaScript
- JS Reference (DevDocs)
- W3Schools JavaScript
- Marquis, M. (2016). JavaScript for Web Designers (1st edition). A Book Apart.
- Niederst Robbins, J. (2018). Learning Web design : a beginner's guide to HTML, CSS, Javascript, and web graphics (Fifth edition.). O'Reilly.
Javascript: Manipulate Styles
- Manipulate Styles / Classes
- Manipulate Content
- Communicate with Web Server to Get and Post data
- Add functionality such as maps, galleries, etc.
Javascript: Manipulate Content
- Manipulate Styles / Classes
- Manipulate Content
- Communicate with Web Server to Get and Post data
- Add functionality such as maps, galleries, etc.
Javascript: Communicate with Web Server
- Manipulate Styles / Classes
- Manipulate Content
- Communicate with Web Server to Get and Post data
- Add functionality such as maps, galleries, etc.

Javascript: Add functionality
- Manipulate Styles / Classes
- Manipulate Content
- Communicate with Web Server to Get and Post data
- Add functionality such as maps, galleries, etc.
Javascript: Add functionality
- Manipulate Styles / Classes
- Manipulate Content
- Communicate with Web Server to Get and Post data
- Add functionality such as maps, galleries, etc.
Code highlighting!
<header>
<h1>Our Solar System</h1>
<nav>
<ul>
<li><a href="#">Planet</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Solar System</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Galaxy</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Universe</a></li>
</ul>
</nav>
</header>
<main>
<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Montes nascetur ridiculus mus mauris vitae ultricies leo integer malesuada.
</p>
</main>header {
background-color: rgb(250, 250, 200);
font-family: sans-serif;
display: flex;
padding: 1rem;
}
header > nav {
flex-grow: 1;
flex-shrink: 1;
}
header nav ul {
list-style-type: none;
padding: 0;
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-end;
}
header nav ul li {
margin-left: 1rem;
}
header nav ul li a {
display: block;
padding: 0.5rem;
text-align: right;
font-weight: bold;
font-size: 1.2rem;
}
header nav ul li a:link,
header nav ul li a:visited {
text-decoration: none;
}
header nav ul li a:hover,
header nav ul li a:active {
text-decoration: underline;
color: white;
background-color: blue;
}
main {
line-height: 1.5;
}
h1,
ul,
li {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
Getting Started with JavaScript
- MDN JavaScript
- JS Reference (DevDocs)
- W3Schools JavaScript
- Marquis, M. (2016). JavaScript for Web Designers (1st edition). A Book Apart.
- Niederst Robbins, J. (2018). Learning Web design : a beginner's guide to HTML, CSS, Javascript, and web graphics (Fifth edition.). O'Reilly.
Some basics
- JS in HTML.
Including JavaScript in HTML withscriptelement, with eithersrcattribute or JS code. - Variables.
Declare variables withletand sometimesconst.
Though you will see the oldervar, which works but is not preferred. - Console is your friend.
Your browser developer tools will be critical to use, and especially the "Console". Log to the console in JS withconsole.log('hello there!'); - When is the code executed?
scriptinheador right before the body close tag -</body>
But it is good practice to rely on specific events! - Objects
- Conditional flow.
if...else - Iterations and Loops.
for...of - Functions - named and anonymous
- DOM (Document Object Model)
- Events, Listeners, and Handlers
load,click,focus,blur,submit,mouseover,mouseout,keypress.
HTML attributes are available, but don't use these.
Add event listeners through JavaScript!
JavaScript and HTML
<script>element- Can reference an external JS file (
srcattribute) - JS code can be within
scriptelement
- Can reference an external JS file (
<script>element can go inhead, but is often placed just before the body close (i.e.</body>) elements.- Note the
<noscript>element for clients without JavaScript.
Script element in HTML5 should have separate end tag!
script element should have an explicit end tag.
Best:
<script src="jquery.js" > </script><script src="jquery.js" /><!-- DON'T DO THIS -->JavaScript in HTML
- External Script
<script src="path/to/javascript/file.js" > </script>- Script within HTML document
<script> /* JavaScript code as content of script element */ </script>
JavaScript Basics
- Variables.
Declare variables withletand sometimesconst.
Though you will see the oldervar, which works but is not preferred. - Console is your friend.
Your browser developer tools will be critical to use, and especially the "Console". Log to the console in JS withconsole.log('hello there!'); - Strings and numbers
- Objects
- Conditional flow.
if...else - Iterations and Loops.
for...ofand.forEach() - Functions - named and anonymous
JavaScript Functions
Named Functions
function davidsFunction() {
}Anonymous Functions
function() {
}Functions with arguments
function calcContrast(color1, color2) {
let contrast;
/* contrast calculation..... */
return(contrast);
}calling a function:
let myContrast = calcContrast('a51c30','ffffff');
Events
- Events - things that happen on page
- Event handler - code that is run when an event happens
- Registering an event listener and handler - linking the code you want to run to an event
Working with Events
addEventListener()DOMContentLoaded- Events:
click,submit,change,focus- And more events:
blur,mouseover,mouseout,keypress,mousedown, and more
- And more events:
addEventListener function lets us add Event Listeners via JavaScript!
let myButton = document.getElementById("makelistbutton");
myButton.addEventListener("click", makeSeasonsList);
Document Object Model (DOM)

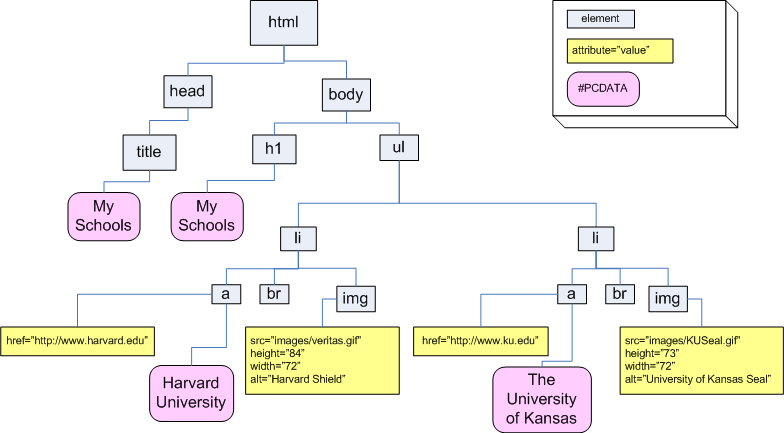
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>My Schools</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>My Schools</h1>
<ul>
<li>
<a href="http://www.harvard.edu/">Harvard University</a><br/>
<img src="images/veritas.gif" alt="Harvard Shield" height="84" width="72"/>
</li>
<li>
<a href="http://www.ku.edu/">University of Kansas</a><br/>
<img src="images/KUSeal.gif" alt="University of Kansas Seal" height="73" width="72"/>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>DOM Visualizer
JavaScript and DOM
querySelectorlets us use "CSS selector" syntax and grab the "first" occurence (so you always get a "single" item).querySelectorAlllets us use "CSS selector" syntax and grab the "all" occurences (so you get a "list" of things).- Also you might see
getElementByIdandgetElementsByTagName getAttributeandsetAttributeclassListandadd,remove,toggle- Various DOM methods to create nodes and add to the node tree (not today!)
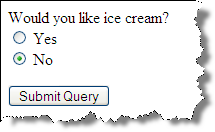
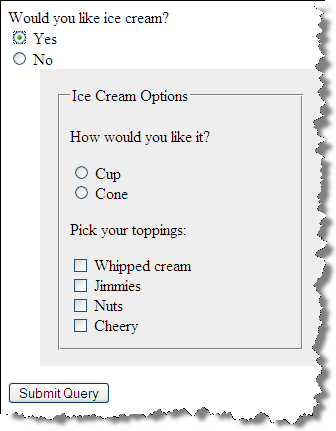
JavaScript and Ice Cream
Exposing Additional Form Elements
Additional relevant form elements are exposed based upon user input.
Here, this is achieved by having the entire form in the markup, with a certain section
hidden via CSS (display: none;). If "Yes" is chosen,
the display property is changed to "block" through JS.
<form method="post" name="ice_cream" id="ice_cream" action="https://cs12.net/form/submit.php">
<fieldset>
<legend>Would you like ice cream? </legend>
<label>
<input type="radio" name="want" id="ic_yes" value="yes"/>
Yes </label>
<label>
<input type="radio" name="want" id="ic_no" value="no"/>
No </label> </fieldset>
<fieldset id="icecream_options">
<legend>Ice Cream Options </legend>
<fieldset>
<legend>What flavor would you like? </legend>
<label>
<input type="radio" id="flavor_vanilla" name="flavor" value="vanilla"/>
Vanilla </label>
<label>
<input type="radio" id="flavor_chocolate" name="flavor" value="choclate"/>
Chocolate </label>
<label>
<input type="radio" id="flavor_chocolate_pb" name="flavor" value="chocolate_peanut_butter"/>
Chocolate Peanut Butter </label>
<label>
<input type="radio" id="flavor_strawberry" name="flavor" value="strawberry"/>
Strawberry </label> </fieldset>
<fieldset>
<legend>Would you like a cup or a cone? </legend>
<label>
<input type="radio" id="container_cup" name="container" value="cup"/>
Cup </label>
<label>
<input type="radio" id="container_cone" name="container" value="cone"/>
Cone </label> </fieldset>
<fieldset>
<legend>What topping do you want? </legend>
<label>
<input type="checkbox" name="toppings" id="toppings_wc" value="whipcream"/>
Whipped cream </label>
<label>
<input type="checkbox" name="toppings" id="toppings_jimmies" value="jimmies"/>
Jimmies </label>
<label>
<input type="checkbox" name="toppings" id="toppings_sprinkles" value="sprinkles"/>
Sprinkles </label>
<label>
<input type="checkbox" name="toppings" id="toppings_nuts" value="nuts"/>
Nuts </label>
<label>
<input type="checkbox" name="toppings" id="toppings_cherry" value="cherry"/>
Cherry </label> </fieldset> </fieldset>
<button type="submit">Submit Order </button>
</form> In style
element
(<style>) within head element:
label {
display: block;
}
input[type=submit],
button[type=submit] {
display: block;
}
form fieldset {
margin-bottom: 1rem;
}
#icecream_options {
border-style: none;
}
button.clicked {
border: 3px solid purple;
}
ul.resourcelist {
border: 2px solid black;
border-radius: 5px;
}
.hidden {
display: none;
}
body {
font-family: helvetica, sans-serif;
margin: 1rem;
line-height: 1.5;
}
In
script element within head element (<script>):
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded',function(){
console.log("dom is loaded!");
let iceCreamOptions = document.querySelector('#icecream_options');
iceCreamOptions.classList.add("hidden");
let wantRadioInputs = document.querySelectorAll("form input[name=want]");
wantRadioInputs.forEach(function(el){
console.log(el);
el.addEventListener("click",function(){
console.log("radio button was just clicked!");
let yesRadio = document.querySelector('#ic_yes');
if (yesRadio.checked == true) {
console.log("Yes is checked!");
iceCreamOptions.classList.remove("hidden");
} else {
console.log("Yes is NOT checked");
iceCreamOptions.classList.add("hidden");
}
})
});
});