Harvard Extension School
Spring 2020
Course Web Site: http://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/
Instructor email: david_heitmeyer@harvard.edu
Course staff email: cscie12@dce.harvard.edu
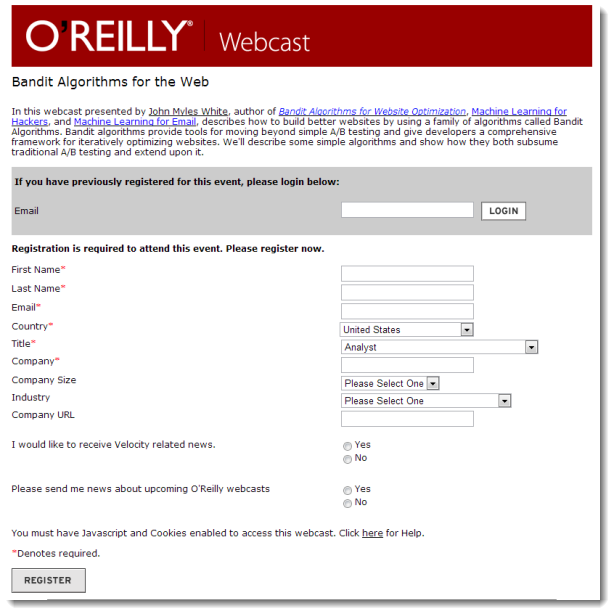
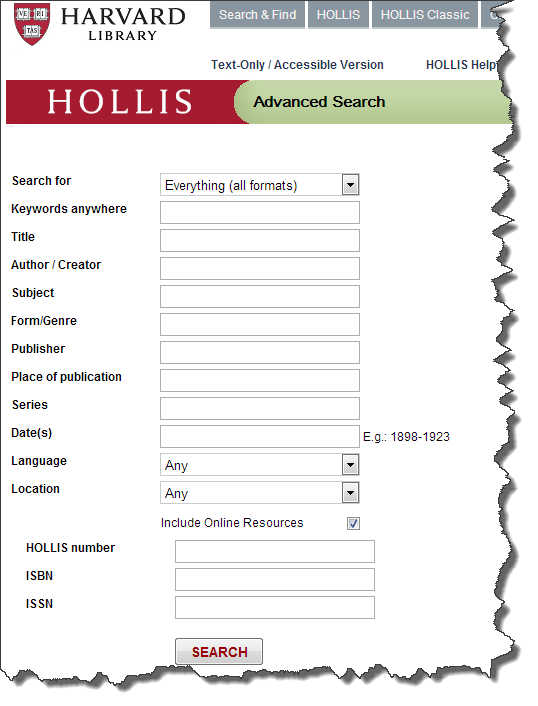
Two elements for forms are in our list of most commonly seen elements:
forminputForms are the "front-end" for the HTTP Client to send information back to the HTTP Server. The submitted information is passed from the HTTP Server to a server-side program that processes the information and produces a response for the browser.


While exploring forms, it is useful to use a simple "echo" CGI program, which will simply echo back the name/value information your form submitted (https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo).
<form method="post" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
Email Address:
<input type="text" name="email"/><br/>
<input type="submit"/>
</form>
http://host/path?param1=value1¶m2=value2¶m3=value3<form method="get" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
Email Address:
<input type="text" name="email"/><br/>
<input type="submit"/>
</form>
<form method="post" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
Email Address:
<input type="text" name="email"/><br/>
<input type="submit"/>
</form>
<form method="get" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
Email Address:
<input type="text" name="email" size="50"/><br/>Year of Birth:
<input type="text" name="year_of_birth" size="50" maxlength="4"/><br/>Year of Birth:
<input type="text" name="year_of_birth_2" size="5" maxlength="4"/><br/>
<input type="submit" name="action" value="Proceed"/>
</form>
<form method="get" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
Email Address:
<input type="text" name="email" size="50"/><br/>Please send me email updates:<br/>
<input type="radio" name="sendupdates" value="yes" checked="checked"/>yes<br/>
<input type="radio" name="sendupdates" value="no"/>no<br/>
<input type="submit" name="action" value="Proceed"/>
</form>
<form method="get" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
What ice cream do you like?<br/>
<input type="checkbox" name="icecream" value="chocolate"/>Chocolate<br/>
<input type="checkbox" name="icecream" value="chocolate peanut butter"/>Chocolate Peanut Butter<br/>
<input type="checkbox" name="icecream" value="vanilla"/>Vanilla<br/>
<input type="checkbox" name="icecream" value="strawberry"/>Strawberry<br/>
<input type="submit" name="action" value="Proceed"/>
</form>
<form method="post" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
<strong>Comments</strong><br/>
<textarea name="comments" rows="10" cols="50">Please enter comments...</textarea><br/>
<input type="submit" name="action" value="Proceed"/>
</form>
<form method="get" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
Select your favorite New England states:<br/>
<select name="state">
<option value="CT">Connecticut</option>
<option value="ME">Maine</option>
<option value="MA">Massachusetts</option>
<option value="NH">New Hampshire</option>
<option value="RI">Rhode Island</option>
<option value="VT">Vermont</option></select><br/>
<input type="submit" name="action" value="Proceed"/>
</form>
Note: because scrollable lists are difficult for users, they are not typically used.
A scrollable list (size attribute) that can have multiple selections (multiple attribute):
<form method="get" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
Select your favorite New England states:<br/>
<select name="state" size="3" multiple="multiple">
<option value="CT">Connecticut</option>
<option value="ME">Maine</option>
<option value="MA">Massachusetts</option>
<option value="NH">New Hampshire</option>
<option value="RI">Rhode Island</option>
<option value="VT">Vermont</option></select><br/>
<input type="submit" name="action" value="Proceed"/>
</form>
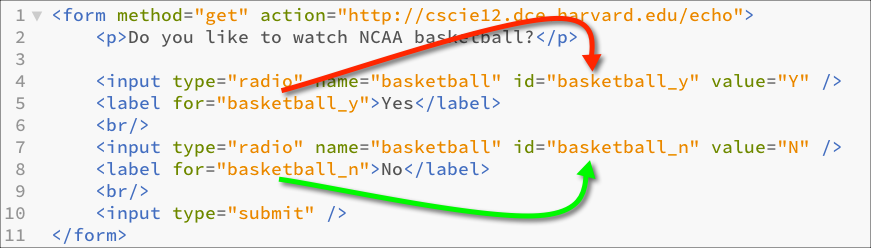
Labels are important for accessible forms.
label element lets us use markup to associate text with an input element.
Using label you can make the association between the text label and the form input explicit, and not just rely on the visual proximity.
<form method="get" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
<p>Do you like to watch NCAA basketball?</p>
<input type="radio" name="basketball" id="basketball_y" value="Y"/><label for="basketball_y">Yes</label><br/>
<input type="radio" name="basketball" id="basketball_n" value="N"/><label for="basketball_n">No</label><br/>
<input type="submit"/>
</form>
<form method="get" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
<div>What ice cream do you like?<br/>
<input type="checkbox" name="icecream" id="icecream_chocolate" value="chocolate"/><label for="icecream_chocolate">Chocolate</label><br/>
<input type="checkbox" name="icecream" id="icecream_cpb" value="chocolate peanut butter"/><label for="icecream_cpb">Chocolate Peanut Butter</label><br/>
<input type="checkbox" name="icecream" id="icecream_vanilla" value="vanilla"/><label for="icecream_vanilla">Vanilla</label><br/>
<input type="checkbox" name="icecream" id="icecream_strawberry" value="strawberry"/><label for="icecream_strawberry">Strawberry</label><br/>
<input type="submit" name="action" value="Proceed"/></div>
</form>
Here we'll cover some additional form features that fit in the "less used" or "advanced" categories.
<form method="post" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
Secret word:
<input type="password" name="secretword" size="10"/><br/>
<input type="submit" name="action" value="Proceed"/>
</form>
<form method="get" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
<input type="hidden" name="myhiddenvariable" value="myhiddenvalue"/>
<input type="submit" name="action" value="Proceed"/>
</form>
With file uploads, the enctype of the form
needs to be multipart/form-data
<form method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
Upload two files:<br/>
<input type="file" name="file1"/><br/>
<input type="file" name="file2"/><br/>
<input type="submit" name="action" value="Upload"/>
</form>
Disabled form elements are used to show something is there, but not currently active.
For example, a form submit might be inactive unless the user has agreed to terms. For that example, we'd need to use JavaScript to change the "disabled" state of the submit input element based on whether the "agree" radio button is selected.
disabled vs disabled="disabled". Note that in the "XML" form of HTML5, the disabled attribute has to have a value, where as in the HTML form of HTML5, the disabled attribute can be on its own.
| XML form of HTML5 | HTML form of HTML5 |
|---|---|
| |
Disabled "submit" input: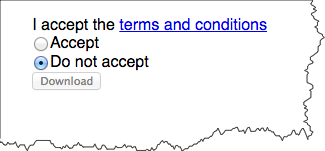
Enabled "submit" input:
HTML Form with basic components
Basic Form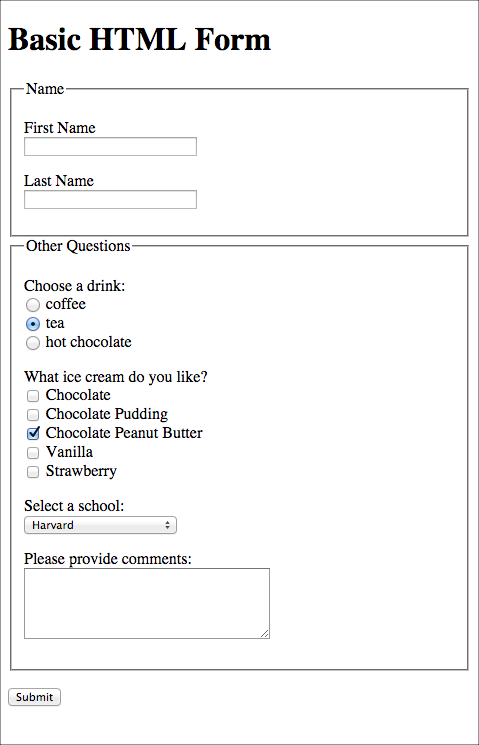
HTML Form with basic components disabled
Basic Form Disabled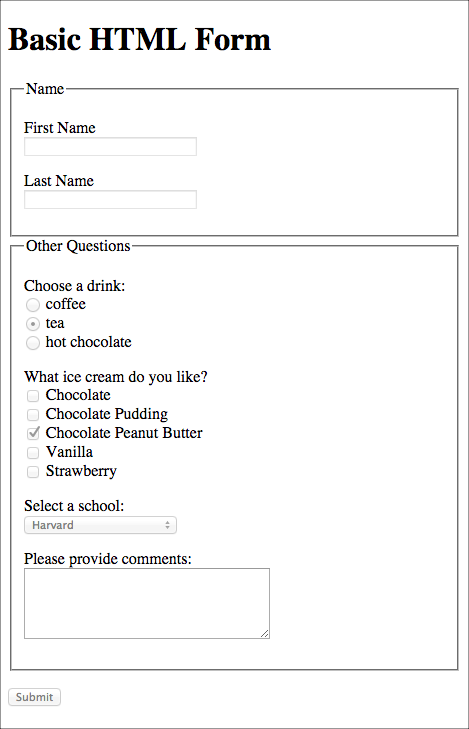
fieldset and legend elements can further help group related input fields.
<form method="get" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
<div><fieldset><legend>Name</legend><label for="fname">First Name</label>
<input type="text" name="fname" id="fname" size="30"/><br/><label for="lname">Last Name</label>
<input type="text" name="lname" id="lname" size="30"/><br/></fieldset><fieldset><legend>Sports</legend><div>Do you enjoy basketball?</div>
<input type="radio" name="basketball" id="basketball_yes" value="Y"/><label for="basketball_yes">Yes</label><br/>
<input type="radio" name="basketball" id="basketball_no" value="N"/><label for="basketball_no">No</label><br/><div>Do you enjoy baseball?</div>
<input type="radio" name="baseball" id="baseball_yes" value="Y"/><label for="baseball_yes">Yes</label><br/>
<input type="radio" name="baseball" id="baseball_no" value="N"/><label for="baseball_no">No</label></fieldset>
<input type="submit"/></div>
</form>
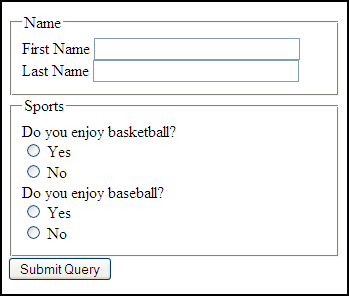
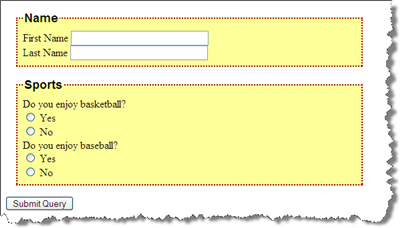
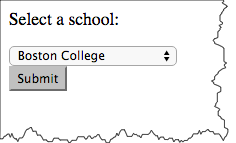
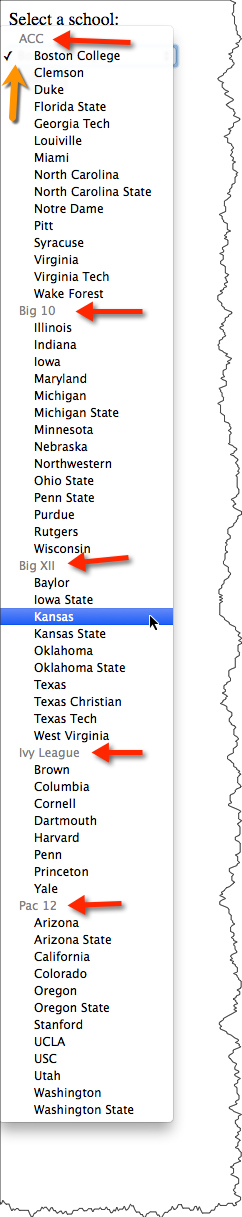
The optgroup element allows you to group a long select list.
<p>Select a school:</p>
<form method="get" action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo">
<select name="school">
<optgroup label="ACC">
<option>Boston College</option>
<option>Clemson</option>
<option>Duke</option>
<option>Florida State</option>
<option>Georgia Tech</option>
<option>Louiville</option>
<option>Miami</option>
<option>North Carolina</option>
<option>North Carolina State</option>
<option>Notre Dame</option>
<option>Pitt</option>
<option>Syracuse</option>
<option>Virginia</option>
<option>Virginia Tech</option>
<option>Wake Forest</option></optgroup>
<optgroup label="Big 10">
<option>Illinois</option>
<option>Indiana</option>
<option>Iowa</option>
<option>Maryland</option>
<option>Michigan</option>
<option>Michigan State</option>
<option>Minnesota</option>
<option>Nebraska</option>
<option>Northwestern</option>
<option>Ohio State</option>
<option>Penn State</option>
<option>Purdue</option>
<option>Rutgers</option>
<option>Wisconsin</option></optgroup>
<optgroup label="Big XII">
<option>Baylor</option>
<option>Iowa State</option>
<option>Kansas</option>
<option>Kansas State</option>
<option>Oklahoma</option>
<option>Oklahoma State</option>
<option>Texas</option>
<option>Texas Christian</option>
<option>Texas Tech</option>
<option>West Virginia</option></optgroup>
<optgroup label="Ivy League">
<option>Brown</option>
<option>Columbia</option>
<option>Cornell</option>
<option>Dartmouth</option>
<option>Harvard</option>
<option>Penn</option>
<option>Princeton</option>
<option>Yale</option></optgroup>
<optgroup label="Pac 12">
<option>Arizona</option>
<option>Arizona State</option>
<option>California</option>
<option>Colorado</option>
<option>Oregon</option>
<option>Oregon State</option>
<option>Stanford</option>
<option>UCLA</option>
<option>USC</option>
<option>Utah</option>
<option>Washington</option>
<option>Washington State</option></optgroup></select><div>
<input type="submit"/></div>
</form>
Select a school:
Placeholder text can:
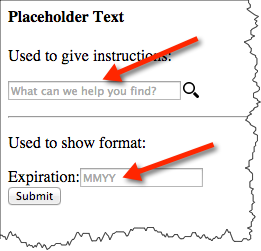
<h4>Placeholder Text</h4><p>Used to give instructions:</p>
<form action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo" method="post">
<input size="30" name="search" type="text" placeholder="What can we help you find?"/>
<input class="searchSubmit" value="Search" type="submit"/>
</form>
<hr/><p>Used to show format:</p>
<form action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo" method="post">
<p><label for="expiration">Expiration:</label>
<input id="expiration" name="expiration" type="text" placeholder="MMYY"/><br/>
<input type="submit"/></p>
</form>
In style
element
(<style type="text/css">) within head element:
input.searchSubmit {
background: url('./images/magnifier12.png') no-repeat;
width: 16px;
height: 16px;
border: none;
margin-left: 2px;
text-indent: -9999em;}Used to give instructions:
Used to show format:
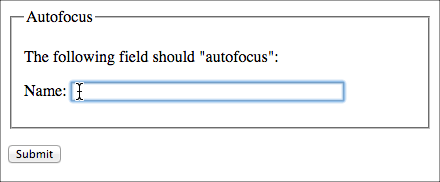
Autofocus will bring the "focus" of the cursor to that field when the page loads. Typically, you would bring focus to the first input field of the form.
XML syntax:
<input type="text" autofocus="autofocus" name="q"/>HTML syntax:
<input type="text" autofocus name="q"><form action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo" method="post">
<fieldset><legend>Autofocus</legend><p>The following field should "autofocus":</p>
<p>Name:
<input size="50" name="name" type="text" autofocus="autofocus"/></p>
</fieldset><p>
<input type="submit"/></p>
</form>
On handheld devices, screen keyboard is optimized for input.
<form action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo" method="post">
<fieldset><legend>Email</legend><p>Email:
<input type="email" name="email_address" size="50"/></p>
</fieldset><p>
<input type="submit"/></p>
</form>
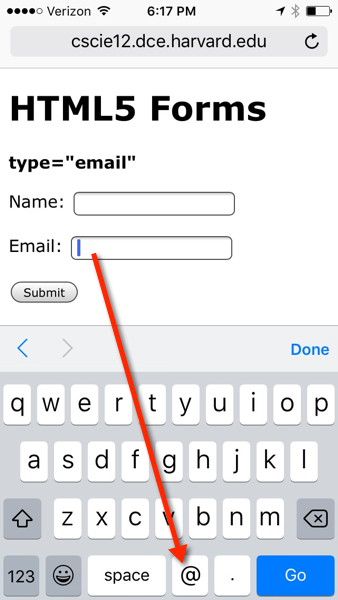
<form action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo" method="post">
<fieldset><legend>URL</legend><p>URL:
<input type="url" name="url" size="50"/></p>
</fieldset><p>
<input type="submit"/></p>
</form>
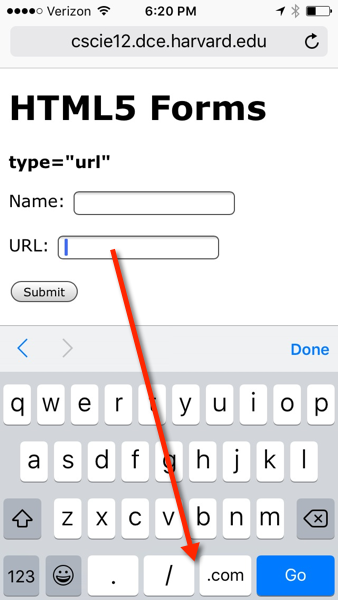
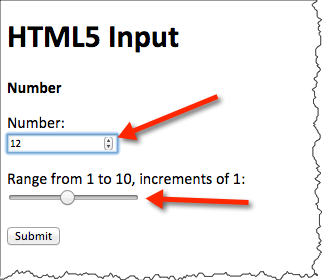
<form action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo" method="post">
<p>Number:<br/>
<input type="number" name="n"/></p>
<p>Range from 1 to 10, increments of 1:<br/>
<input type="range" min="1" max="10" step="1" name="r"/></p>
<p>
<input type="submit"/></p>
</form>
<form action="https://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/echo" method="post">
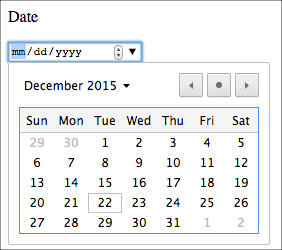
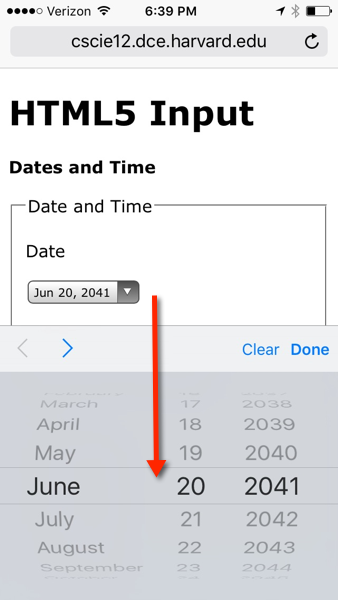
<fieldset><legend>Date and Time</legend><p>Date</p>
<p>
<input type="date" name="my_date"/></p>
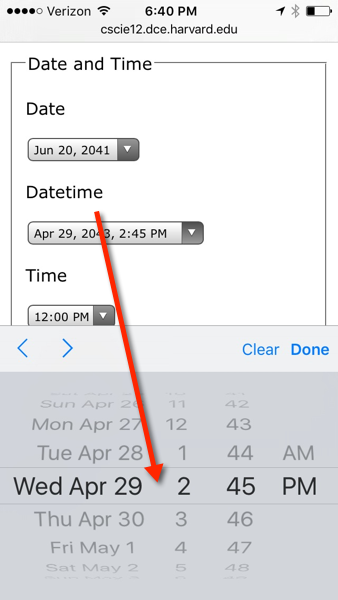
<p>Datetime-local</p>
<p>
<input type="datetime-local" name="my_datetime"/></p>
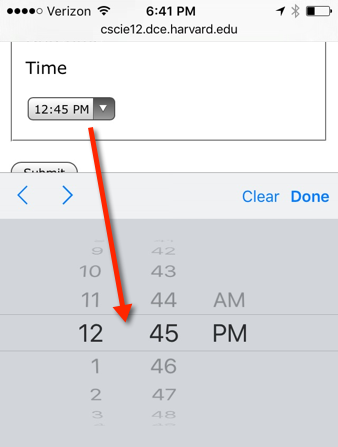
<p>Time</p>
<p>15 minute steps:
<input type="time" name="my_time_15" step="900" value="12:00"/></p>
<p>1 minute steps:
<input type="time" name="my_time_1" step="60" value="12:00"/></p>
<p>1 second steps:
<input type="time" name="my_time_1s" step="1" value="12:00"/></p>
</fieldset><p>
<input type="submit"/></p>
</form>
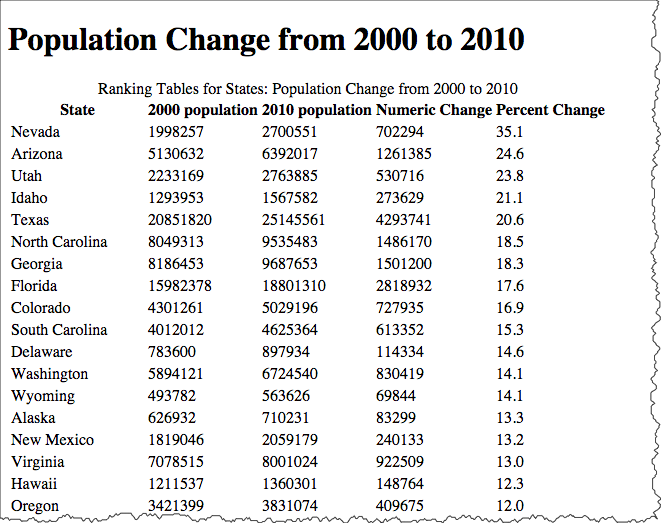
See: Tabular Data from HTML5 Specification
table ,
caption ,
colgroup ,
col ,
tbody ,
thead ,
tfoot ,
tr ,
td ,
th
<table>
<caption>A table</caption>
<tr>
<th>Column 1</th>
<th>Column 2</th>
<th>Column 3</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>row 1 column 1</td>
<td>row 1 column 2</td>
<td>row 1 column 3</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>row 2 column 1</td>
<td>row 2 column 2</td>
<td>row 2 column 3</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>row 3 column 1</td>
<td>row 3 column 2</td>
<td>row 3 column 3</td>
</tr>
</table>
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
|---|---|---|
| row 1 column 1 | row 1 column 2 | row 1 column 3 |
| row 2 column 1 | row 2 column 2 | row 2 column 3 |
| row 3 column 1 | row 3 column 2 | row 3 column 3 |
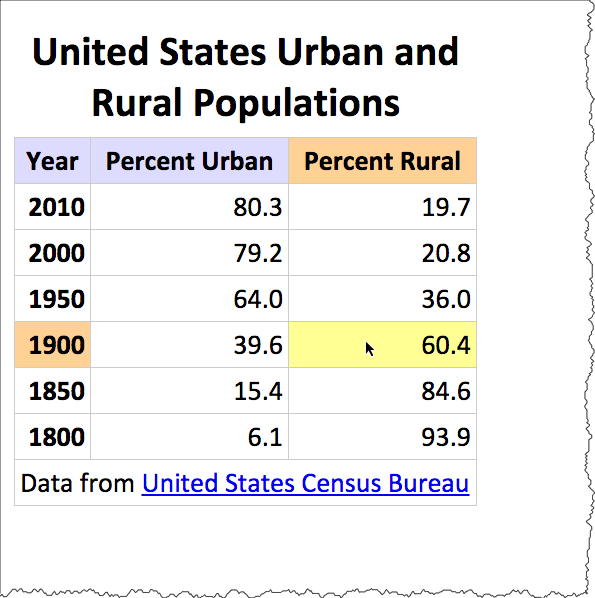
Data from the US Census Bureau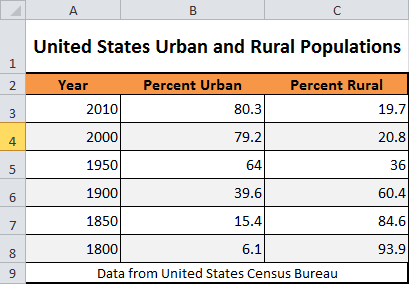
<p>United States Urban and Rural Populations</p>
<table>
<tr>
<td>Year</td>
<td>Percent Urban</td>
<td>Percent Rural</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>2010</th>
<td>80.3</td>
<td>19.7</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>2000</th>
<td>79.2</td>
<td>20.8</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>1950</th>
<td>64.0</td>
<td>36.0</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>1900</th>
<td>39.6</td>
<td>60.4</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>1850</th>
<td>15.4</td>
<td>84.6</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>1800</th>
<td>6.1</td>
<td>93.9</td>
</tr>
</table>
<p>Data from<a href="http://www.census.gov/">United States Census Bureau</a></p>
United States Urban and Rural Populations
| Year | Percent Urban | Percent Rural |
| 2010 | 80.3 | 19.7 |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 79.2 | 20.8 |
| 1950 | 64.0 | 36.0 |
| 1900 | 39.6 | 60.4 |
| 1850 | 15.4 | 84.6 |
| 1800 | 6.1 | 93.9 |
Data from United States Census Bureau
<table summary="This table shows the percentage of the United States population that lived in urban and rural areas from 1800 to 2000.">
<caption>United States Urban and Rural Populations</caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Year</th>
<th>Percent Urban</th>
<th>Percent Rural</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tfoot>
<tr>
<td colspan="3">Data from<a href="http://www.census.gov/">United States Census Bureau</a></td>
</tr>
</tfoot><tbody>
<tr>
<th>2010</th>
<td>80.3</td>
<td>19.7</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>2000</th>
<td>79.2</td>
<td>20.8</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>1950</th>
<td>64.0</td>
<td>36.0</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>1900</th>
<td>39.6</td>
<td>60.4</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>1850</th>
<td>15.4</td>
<td>84.6</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>1800</th>
<td>6.1</td>
<td>93.9</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
| Year | Percent Urban | Percent Rural |
|---|---|---|
| Data from United States Census Bureau | ||
| 2010 | 80.3 | 19.7 |
| 2000 | 79.2 | 20.8 |
| 1950 | 64.0 | 36.0 |
| 1900 | 39.6 | 60.4 |
| 1850 | 15.4 | 84.6 |
| 1800 | 6.1 | 93.9 |
Semantics lets us selectively manipulate parts of the table -- whether for style or function.
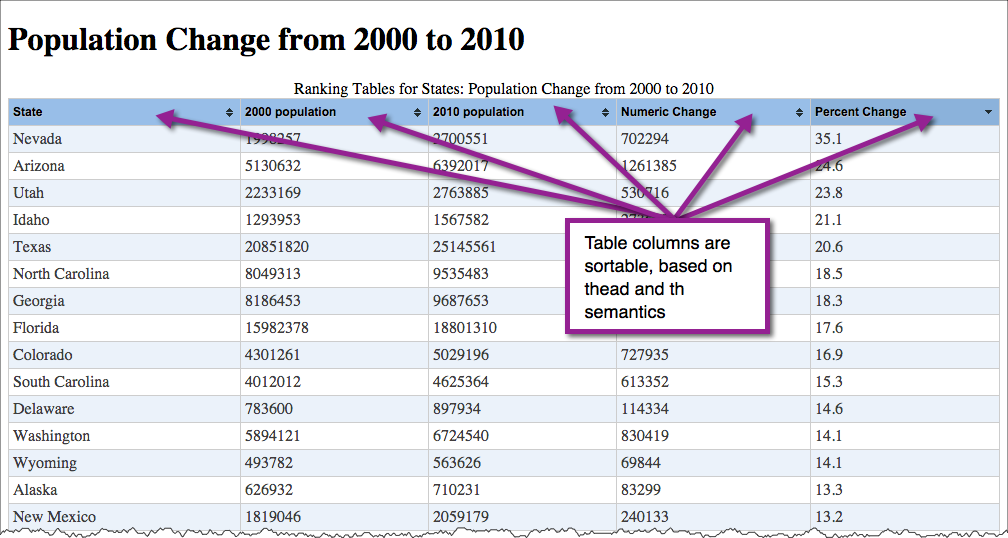
col and colgroup elements can be used to as a way to apply styles (style or class attribute) to columns.
<table>
<caption>United States Urban and Rural Populations</caption>
<colgroup span="1">
<col span="1" style="background-color: lightsalmon;"/>
<col span="2" style="background-color: wheat;"/>
</colgroup>
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">Year</th>
<th scope="col">Percent Urban</th>
<th scope="col">Percent Rural</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<th scope="row">2010</th>
<td>80.3</td>
<td>19.7</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">2000</th>
<td>79.2</td>
<td>20.8</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">1950</th>
<td>64.0</td>
<td>36.0</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">1900</th>
<td>39.6</td>
<td>60.4</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">1850</th>
<td>15.4</td>
<td>84.6</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">1800</th>
<td>6.1</td>
<td>93.9</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
| Year | Percent Urban | Percent Rural |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 80.3 | 19.7 |
| 2000 | 79.2 | 20.8 |
| 1950 | 64.0 | 36.0 |
| 1900 | 39.6 | 60.4 |
| 1850 | 15.4 | 84.6 |
| 1800 | 6.1 | 93.9 |
The "scope" attribute can be used to associate header information with columns and rows (and also column groups and row groups).
<table>
<caption>United States Urban and Rural Populations</caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">Year</th>
<th scope="col">Percent Urban</th>
<th scope="col">Percent Rural</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tfoot>
<tr>
<td colspan="3">Data from<a href="http://www.census.gov/">United States Census Bureau</a></td>
</tr>
</tfoot><tbody>
<tr>
<th scope="row">2010</th>
<td>80.3</td>
<td>19.7</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">2000</th>
<td>79.2</td>
<td>20.8</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">1950</th>
<td>64.0</td>
<td>36.0</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">1900</th>
<td>39.6</td>
<td>60.4</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">1850</th>
<td>15.4</td>
<td>84.6</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th scope="row">1800</th>
<td>6.1</td>
<td>93.9</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
| Year | Percent Urban | Percent Rural |
|---|---|---|
| Data from United States Census Bureau | ||
| 2010 | 80.3 | 19.7 |
| 2000 | 79.2 | 20.8 |
| 1950 | 64.0 | 36.0 |
| 1900 | 39.6 | 60.4 |
| 1850 | 15.4 | 84.6 |
| 1800 | 6.1 | 93.9 |
The "headers" attribute can also be used to associate header information with columns and rows. This is typically used in more complicated tables.
id attribute. Note the use of the "id" attribute. This is an attribute that can be applied to most any HTML element. Values for "id" must be unique throughout the document.
The value of "headers" is a space-separated list of IDREFS (references to "id" names in the document).

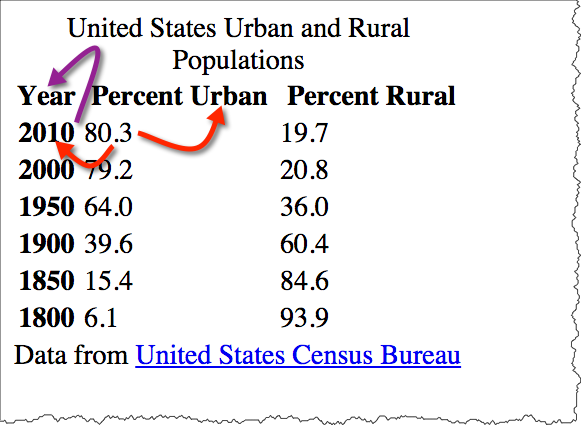
<table>
<caption>United States Urban and Rural Populations</caption>
<thead>
<tr>
<th id="year">Year</th>
<th id="urban">Percent Urban</th>
<th id="rural">Percent Rural</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tfoot>
<tr>
<td colspan="3">Data from<a href="http://www.census.gov/">United States Census Bureau</a></td>
</tr>
</tfoot><tbody>
<tr>
<th id="y2010" headers="year">2010</th>
<td headers="y2010 urban">80.3</td>
<td headers="y2010 rural">19.7</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th id="y2000" headers="year">2000</th>
<td headers="y2000 urban">79.2</td>
<td headers="y2000 rural">20.8</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th id="y1950" headers="year">1950</th>
<td headers="y1950 urban">64.0</td>
<td headers="y1950 ruran">36.0</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th id="y1900" headers="year">1900</th>
<td headers="y1900 urban">39.6</td>
<td headers="y1900 rural">60.4</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th id="y1850" headers="year">1850</th>
<td headers="y1850 urban">15.4</td>
<td headers="y1850 rural">84.6</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<th id="y1800" headers="year">1800</th>
<td headers="y1800 urban">6.1</td>
<td headers="y1800 rural">93.9</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
| Year | Percent Urban | Percent Rural |
|---|---|---|
| Data from United States Census Bureau | ||
| 2010 | 80.3 | 19.7 |
| 2000 | 79.2 | 20.8 |
| 1950 | 64.0 | 36.0 |
| 1900 | 39.6 | 60.4 |
| 1850 | 15.4 | 84.6 |
| 1800 | 6.1 | 93.9 |
Once semantic markup is in place, adding function with JavaScript becomes much easier. For example, we can write some JavaScript to highlight the column/row headings based on the presence of scope or headers attributes.
Live Example of Table Highlighting
HTML5 defines elements that can be used to represent sections (New to HTML5):
body - represents the main content of the documentarticle - represents a self-contained composition within a documentsection - a generic section of a documentnav - represents a section with navigation linksaside - tangentially related (analagous to a sidebar for printed material)h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6 - headings for sectionshgroup - used to group a set of headingsheader - represents a group of introductory or navigational aidsfooter - represents a footer for its sectionaddress - represents contact informatinSee: Usage Summary for Section Elements
bodyheaderfooternav

The markup page references an external stylesheet document.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Our Solar System</title>
<!-- the link element is used to reference a stylesheet -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="solarsystem.css" type="text/css"/>
...cut...The CSS file contains style rules for the document (solarsystem.css)
@import url(js/fancybox/jquery.fancybox-1.3.1.css);
body {
margin-left: 10%;
margin-top: 1em;
margin-right: 10%;
background: #ffd;
font-family: Calibri,Arial,sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-family: Calibri,Arial, sans-serif;
color: #333;
border-bottom: thin dotted black;
}
ul.gallery {
list-style: none;
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
ul.gallery li {
margin-top: 1em;
font-size: 1.25em;
height: 170px;
width: 150px;
float: left;
text-align: center;
border: thin dotted black;
margin: 10px;
padding: 10px;
}
ul.gallery li img { border: none; }
p.credits {
clear: both;
border: none;
margin-top: 20px;
padding: 1em;
font-size: smaller;
}
a:link,a:visited {text-decoration: none; color: blue; }
a:hover { text-decoration: underline; }
a:active { border: none; text-decoration: none; }







Harvard Summer School 2011 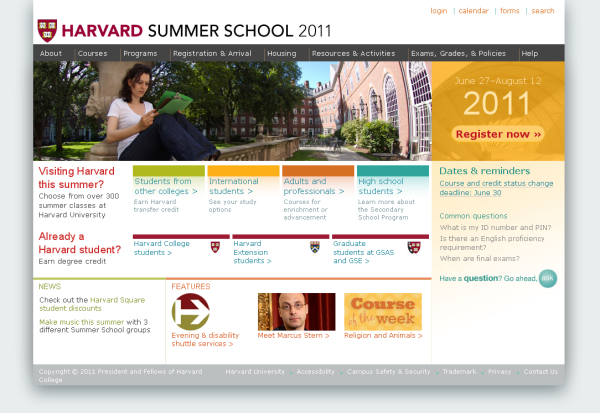 | With CSS disabled: 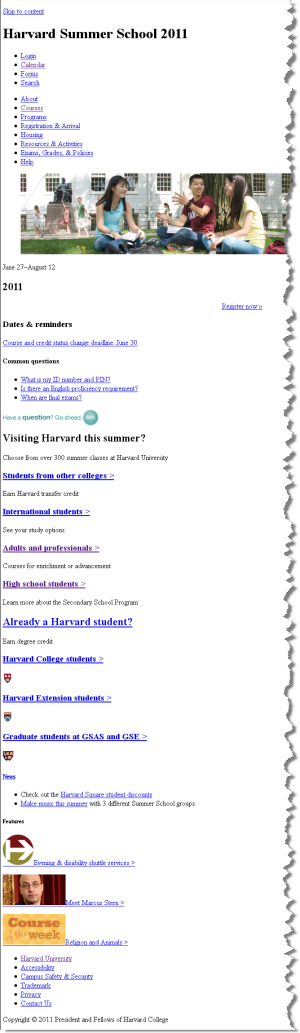 |
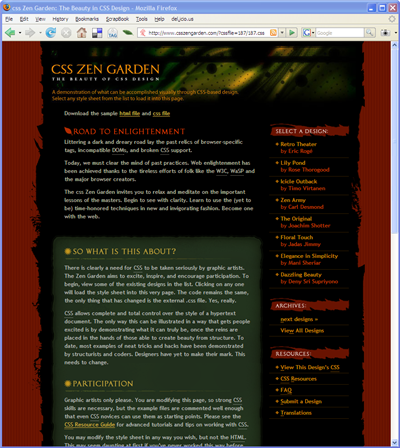
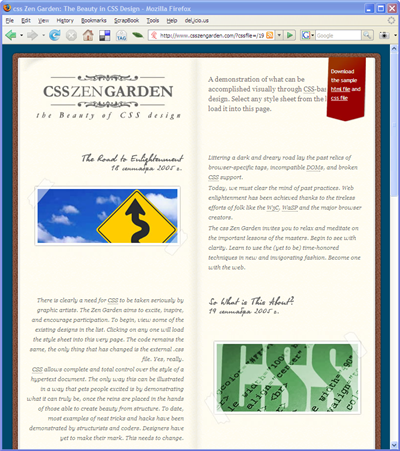
css Zen Garden: The Beauty in CSS Design. A demonstration of what can be accomplished visually through CSS-based desgin.
 |  |
 | 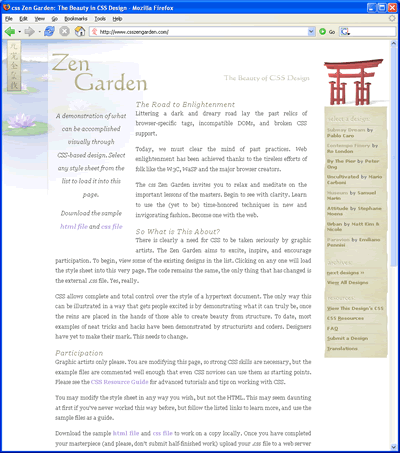 |
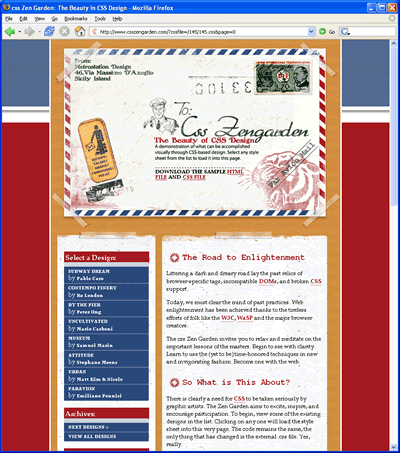 | 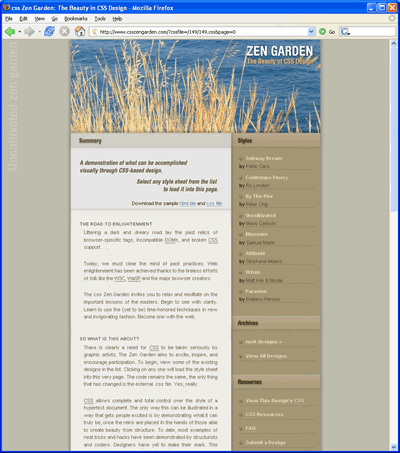 |
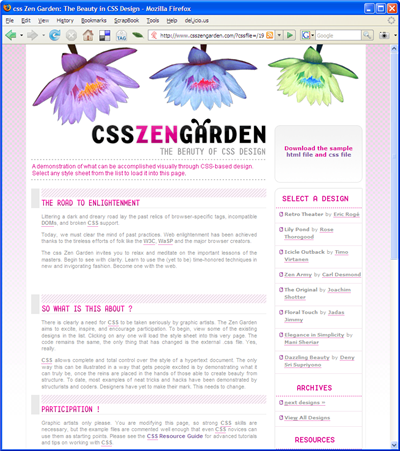 |  |




<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.</p>
In style
element
(<style type="text/css">) within head element:
p {
color: red;
background-color: blue;
}
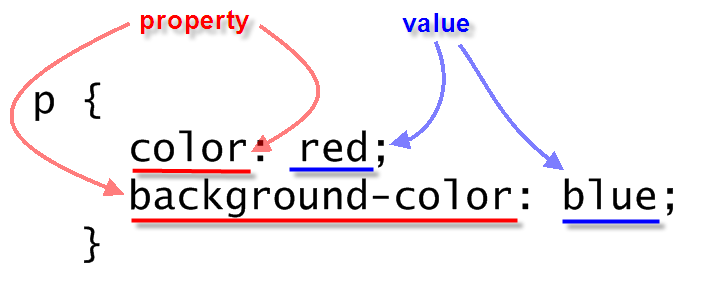
Three ways to bind CSS rules to HTML markup:
style attribute in element<style> element in HTML head<link> element in HTML head<p style="color: black; background-color: teal; padding: 1em; font-family: helvetica, sans-serif; text-align: justify; margin: 2em;">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.</p>
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.

<p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.</p>
In style
element
(<style type="text/css">) within head element:
p {
color: black;
background-color: teal;
padding: 1em;
font-family: helvetica, sans-serif;
text-align: justify;
margin: 2em;
}
So the full page looks like:
<html>
<head>
<title>CSCIE-12 CSS Example</title>
<style type="text/css">
p {
color: black;
background-color: teal;
padding: 1em;
font-family: helvetica, sans-serif;
text-align: justify;
margin: 2em;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec
facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit.
Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante
sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</p>
</body>
</html><p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.</p>
In
head element:
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="example32.css"/>p {
color: black;
background-color: teal;
padding: 1em;
font-family: helvetica, sans-serif;
text-align: justify;
margin: 2em;
}

The full source:
<html>
<head>
<title>CSCIE-12 CSS Example</title>
<link href="example37.css" type="text/css" rel="stylesheet"/>
</head>
<body>
<p>
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec
facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit.
Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante
sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
</p>
</body>
</html>Rules can be combined. The following two sets of style rules would produce identical results. Rules can be listed separately:
p {color: black;}
p {background-color: teal;}
p {padding: 1em;}
p {margin: 1em;}
p {font-family: helvetica, sans-serif;}
p {text-align: justify;}Or, rules can be grouped. Property:Value pairs need to be separated by a semicolon.
p {
color: black;
background-color: teal;
padding: 1em;
margin: 1em;
font-family: helvetica, sans-serif;
text-align: justify;
}h1 { color: maroon; }
h2 { color: maroon; }
h3 { color: maroon; }
h4 { color: maroon; }
h5 { color: maroon; }
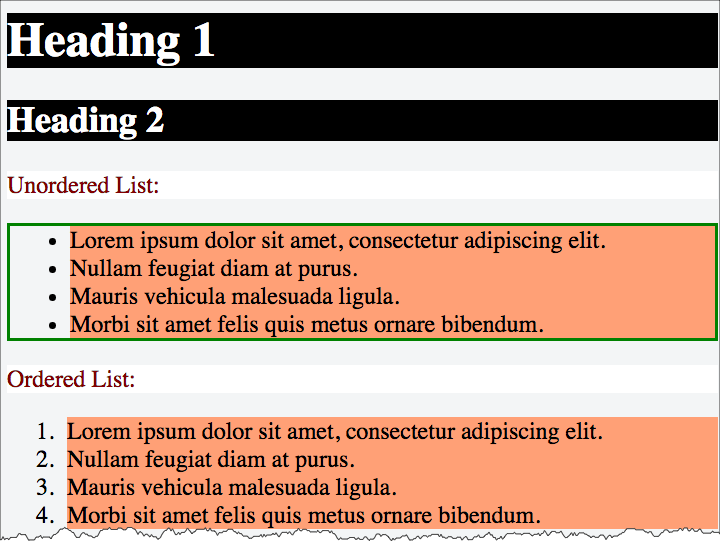
h6 { color: maroon; }h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6 { color: maroon; }p {
background-color: white;
color: maroon;
}
ul {
border: medium solid green;
}
li {
background-color: lightsalmon;
}
h1,
h2,
h3 {
background-color: black;
color: white;
}
The class and id attributes of HTML elements can be used in conjunction with styles.
Class names are referenced in CSS as .classname, and may or may not have an element name preceding the period (.classname or element.classname.
Likewise, id names are referenced in CSS as #idref, and may or may not have an element name preceding the period (#idref or element#idref.
<div>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.</div><div class="withstyle">Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.</div><div class="warn">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.</div><div>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,<span class="warn">consectetuer adipiscing elit</span>. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.</div><div id="legalese">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.</div> In style
element
(<style type="text/css">) within head element:
div
{
background-color: white;
color: black;
font-family: times;
margin: 0.5em;
padding: 0.5em;
}
div.withstyle
{
background-color: olive;
color: navy;
font-family: sans-serif;
margin: 0.5em;
padding: 0.5em;
}
.warn
{
background-color: yellow;
color: red;
font-weight: bold;
}
#legalese
{
color: #cccccc;
font-size: 0.6em;
}
id names are referenced in CSS as #idref, and may or may not have an element name preceding the period (#idref or element#idref.
<div id="header">put in header information here</div><div id="main"><!-- main content -->Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.</div><div id="footer">put in footer information here</div> In style
element
(<style type="text/css">) within head element:
#main {
background-color: blue;
color: white;
border-color: green;
border-width: thick;
border-style: solid;
} 
selector1 selector2 { ...rules... }
<div><em>Emphasized text</em>outside of<strong>li</strong>appear "normal".<ul>
<li><em>Emphasized text</em>within<strong>li</strong>have a different style.</li>
</ul></div> In style
element
(<style type="text/css">) within head element:
li em { color: red; background-color: navy;}
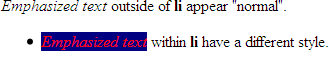
CSS Level 1 lists 53 properties that let you style properties of:
CSS Level 2.1 lists 115 properties.
CSS Level 1 lists 53 properties.
| CSS Level 2.1 lists 115 properties.
|
<div>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet,<em>consectetuer adipiscing elit</em>. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.<ul>
<li>Lorem</li>
<li>Ipsum</li>
<li>Dolor</li>
</ul></div><p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.</p>
<ul>
<li>Lorem</li>
<li>Ipsum</li>
<li>Dolor</li>
</ul> In style
element
(<style type="text/css">) within head element:
body { color: navy; }
em { color: red; }
div { color: green; }

UA = User-Agent = HTTP Client = Web Browser
html, address,
blockquote,
body, dd, div,
dl, dt, fieldset, form,
frame, frameset,
h1, h2, h3, h4,
h5, h6, noframes,
ol, p, ul, center,
dir, hr, menu, pre { display: block }
li { display: list-item }
head { display: none }
table { display: table }
tr { display: table-row }
thead { display: table-header-group }
tbody { display: table-row-group }
tfoot { display: table-footer-group }
col { display: table-column }
colgroup { display: table-column-group }
td, th { display: table-cell; }
caption { display: table-caption }
th { font-weight: bolder; text-align: center }
caption { text-align: center }
body { margin: 8px; line-height: 1.12 }
h1 { font-size: 2em; margin: .67em 0 }
h2 { font-size: 1.5em; margin: .75em 0 }
h3 { font-size: 1.17em; margin: .83em 0 }
h4, p,
blockquote, ul,
fieldset, form,
ol, dl, dir,
menu { margin: 1.12em 0 }
h5 { font-size: .83em; margin: 1.5em 0 }
h6 { font-size: .75em; margin: 1.67em 0 }
h1, h2, h3, h4,
h5, h6, b,
strong { font-weight: bolder }
blockquote { margin-left: 40px; margin-right: 40px }
i, cite, em,
var, address { font-style: italic }
pre, tt, code,
kbd, samp { font-family: monospace }
pre { white-space: pre }
button, pre,
input, object,
select { display:inline-block; }
big { font-size: 1.17em }
small, sub, sup { font-size: .83em }
sub { vertical-align: sub }
sup { vertical-align: super }
table { border-spacing: 2px; }
thead, tbody,
tfoot { vertical-align: middle }
td, th { vertical-align: inherit }
s, strike, del { text-decoration: line-through }
hr { border: 1px inset }
ol, ul, dir,
menu, dd { margin-left: 40px }
ol { list-style-type: decimal }
ol ul, ul ol,
ul ul, ol ol { margin-top: 0; margin-bottom: 0 }
u, ins { text-decoration: underline }
br:before { content: "\A" }
:before, :after { white-space: pre-line }
center { text-align: center }
abbr, acronym { font-variant: small-caps; letter-spacing: 0.1em }
:link, :visited { text-decoration: underline }
:focus { outline: thin dotted invert }
/* Begin bidirectionality settings (do not change) */
BDO[DIR="ltr"] { direction: ltr; unicode-bidi: bidi-override }
BDO[DIR="rtl"] { direction: rtl; unicode-bidi: bidi-override }
*[DIR="ltr"] { direction: ltr; unicode-bidi: embed }
*[DIR="rtl"] { direction: rtl; unicode-bidi: embed }
@media print {
h1 { page-break-before: always }
h1, h2, h3,
h4, h5, h6 { page-break-after: avoid }
ul, ol, dl { page-break-before: avoid }
}BODY {
margin: 1em;
font-family: serif;
line-height: 1.1;
background: white;
color: black;
}
H1, H2, H3, H4, H5, H6, P, UL, OL, DIR, MENU, DIV,
DT, DD, ADDRESS, BLOCKQUOTE, PRE, BR, HR, FORM, DL {
display: block }
B, STRONG, I, EM, CITE, VAR, TT, CODE, KBD, SAMP,
IMG, SPAN { display: inline }
LI { display: list-item }
H1, H2, H3, H4 { margin-top: 1em; margin-bottom: 1em }
H5, H6 { margin-top: 1em }
H1 { text-align: center }
H1, H2, H4, H6 { font-weight: bold }
H3, H5 { font-style: italic }
H1 { font-size: xx-large }
H2 { font-size: x-large }
H3 { font-size: large }
B, STRONG { font-weight: bolder } /* relative to the parent */
I, CITE, EM, VAR, ADDRESS, BLOCKQUOTE { font-style: italic }
PRE, TT, CODE, KBD, SAMP { font-family: monospace }
PRE { white-space: pre }
ADDRESS { margin-left: 3em }
BLOCKQUOTE { margin-left: 3em; margin-right: 3em }
UL, DIR { list-style: disc }
OL { list-style: decimal }
MENU { margin: 0 } /* tight formatting */
LI { margin-left: 3em }
DT { margin-bottom: 0 }
DD { margin-top: 0; margin-left: 3em }
HR { border-top: solid } /* 'border-bottom' could also have been used */
A:link { color: blue } /* unvisited link */
A:visited { color: red } /* visited links */
A:active { color: lime } /* active links */
/* setting the anchor border around IMG elements
requires contextual selectors */
A:link IMG { border: 2px solid blue }
A:visited IMG { border: 2px solid red }
A:active IMG { border: 2px solid lime }
body {
font-family: garamond, times, serif;
}<div style="font-family: garamond, times, serif;">Garamond, Times, or serif (generic family)</div><div style="font-family: calibri, arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">Calibri, Arial, Helvetica or sans-serif (generic family)</div><div style="font-family: lucida console, courier, monospace;">Lucida Console, Courier or monospace (generic family)</div><div style="font-family: fantasy;">Fantasy (generic family)</div><div style="font-family: cursive;">Cursive (generic family)</div>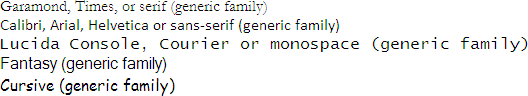
em {
font-style: italic;
}<div style="font-style: normal;">Normal font-style</div><div style="font-style: italic;">Italic font-style</div><div style="font-style: oblique;">Oblique font-style</div><div style="font-variant: small-caps;">This should be rendered in small-caps.<div style="font-variant: normal;">Here we revert to "normal".</div></div>strong {
font-weight: bold;
}<div>font-weight can be used to make<span style="font-weight: bold">text appear bold</span>.</div><div style="font-size: 8pt;">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.</div><div style="font-size: 120%;">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.</div><div style="font-size: 1.5em;">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci.</div>
As a general guideline with CSS, relative measurements are better than absolute measurements.
xx-small | x-small | small | medium | large | x-large | xx-largerem - relative to the html em (root em)larger | smallerThe font shorthand property allows you to set:[font-style | font-variant | font-weight ]? font-size[/line-height]? font-family
<div>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.</div> In style
element
(<style type="text/css">) within head element:
body {
font: normal normal normal x-large/200% arial, helvetica, sans-serif;
}
Align blocks of text left, right, center, and justified.
<div style="margin-left: 30%; margin-right: 30%;"><p style="text-align: left">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.</p>
<p style="text-align: center">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.</p>
<p style="text-align: right">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.</p>
<p style="text-align: justify">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.</p>
</div>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.

1.0em 10%url('../images/banner.png')aqua#ffd#60ae9frgb(24,50,255)rgb(5%,20%,75%)
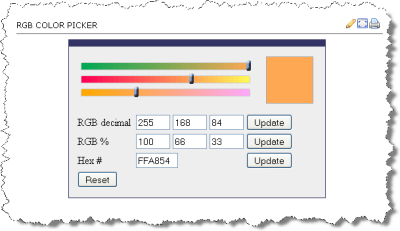
The following are all equivalent ways of defining a shade of orange:
|
<div style="background-color: rgb(100%,66%,33%); padding: 1em; ; margin: 1em;">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit.<br/>rgb(100%,66%,33%)</div><div style="background-color: #ffa854; padding: 1em; margin: 1em; ">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit.<br/>#ffa854</div><div style="background-color: rgb(255,168,84); padding: 1em; ; margin: 1em;">Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit.<br/>rgb(255,168,84)</div><input type="color" />And a few that aren't listed at BrowseHappy.com:
| Web Browser | Layout Engine |
|---|---|
| Google Chrome | Blink (fork of Webkit) |
| Apple Safari | Webkit |
| Mozilla Firefox | Gecko |
| Microsoft | EdgeHTML (Edge) Trident (IE) |
| Opera | Blink (fork of Webkit) |
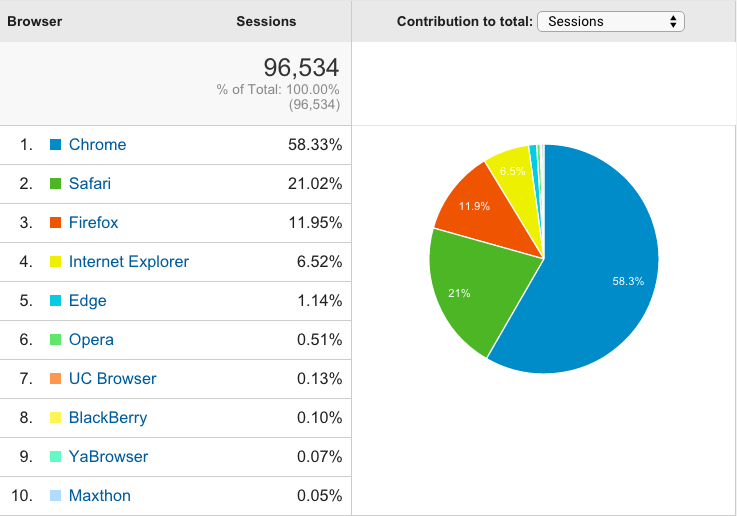
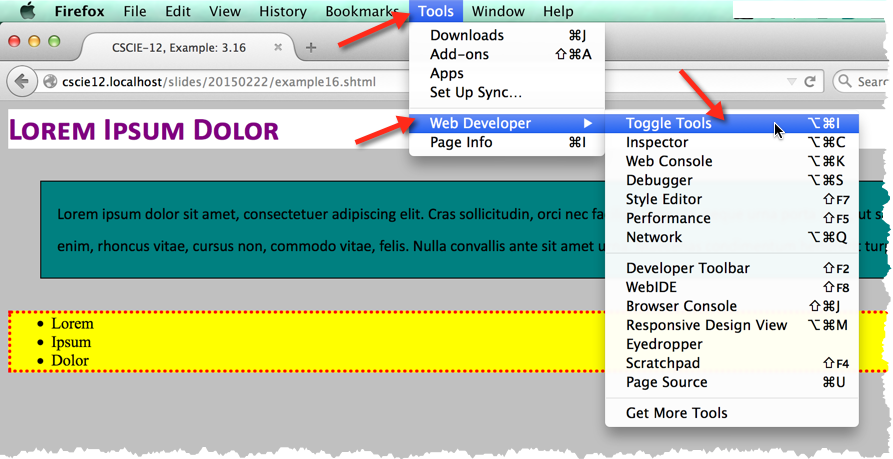
Note that Firebug functionality is now incorporated directly into Firefox. See: Firefox Developer Tools.
Access Developer Tools using the Firefox menu and then select "Developer"
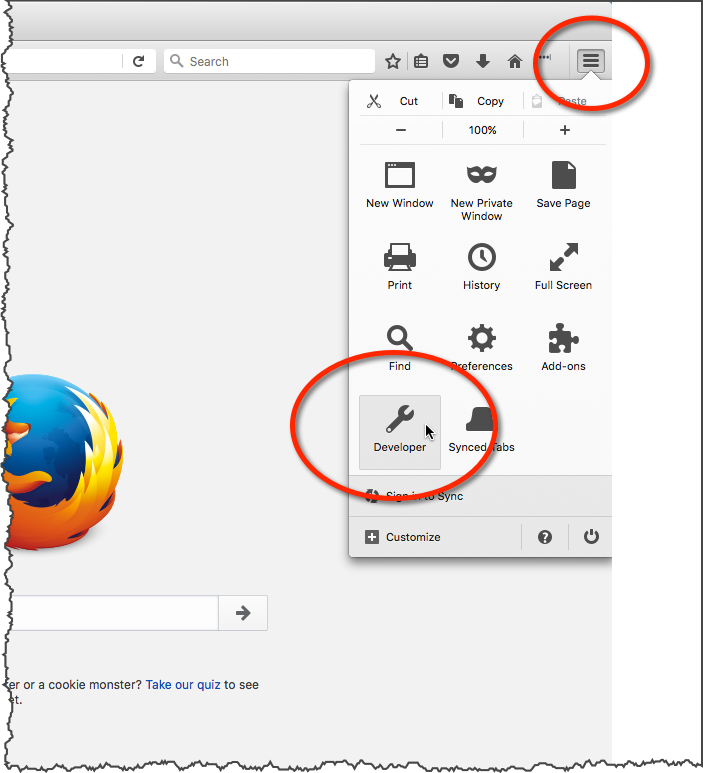
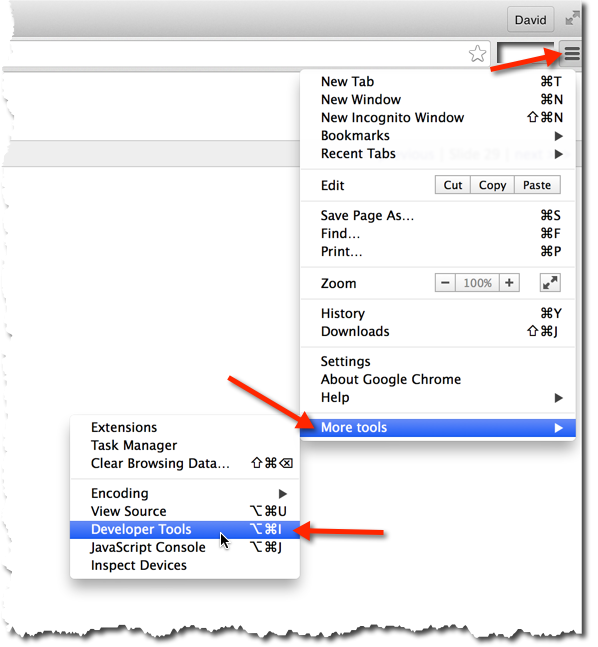
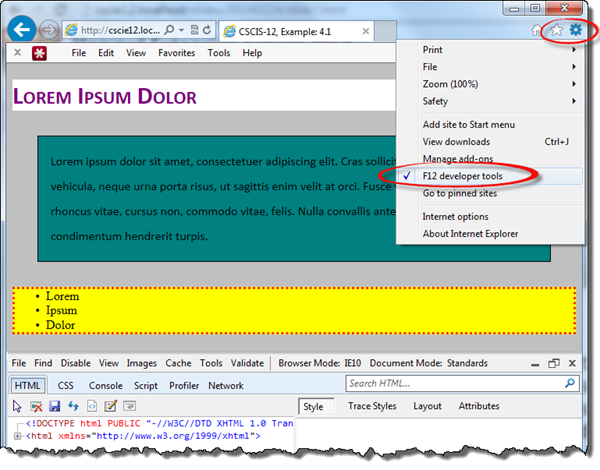
Safari Web Inspector - Getting Started
Safari → Preferences → Advanced → Show Develop menu in menu bar
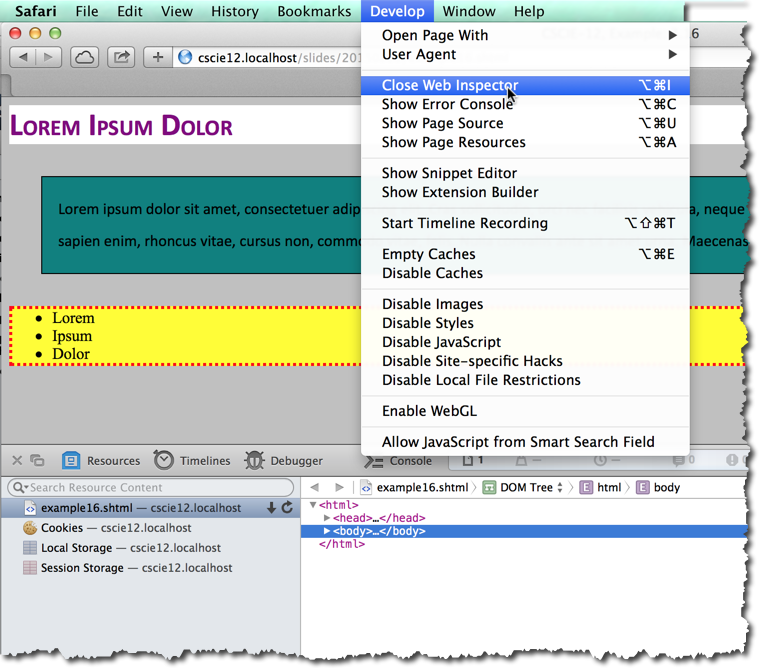
<h1>Lorem Ipsum Dolor</h1><p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Cras sollicitudin, orci nec facilisis vehicula, neque urna porta risus, ut sagittis enim velit at orci. Fusce velit. Integer sapien enim, rhoncus vitae, cursus non, commodo vitae, felis. Nulla convallis ante sit amet urna. Maecenas condimentum hendrerit turpis.</p>
<ul>
<li>Lorem</li>
<li>Ipsum</li>
<li>Dolor</li>
</ul> In style
element
(<style type="text/css">) within head element:
body {
background-color: silver;
font-family: calibri, arial, helvetica, sans-serif;
}
p {
line-height: 200%;
border: thin solid black;
padding: 1em;
margin: 2em;
background-color: teal;
}
ul {
border: medium dotted red;
background-color: yellow;
font-family: Times New Roman, Times, serif;
}
h1 {
color: purple;
background-color: white;
font-variant: small-caps;
}
Copyright © David Heitmeyer