
Harvard University Extension School
Spring 2018
Course Web Site: http://cscie12.dce.harvard.edu/
Instructor email: david_heitmeyer@harvard.edu
Course staff email: cscie12@dce.harvard.edu
Two ways to deal with fonts:
Note:
@font-face in CSS
link element in head of HTMLMore resources:
Typically used for fonts that are served from your web server.
@font-face {
font-family:Capture;
src:url('resources/fonts/Capture_it.ttf');
/* could have multiple src properties that reference
different font formats */
}
h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6 {
font-weight:400;
font-family:Capture, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size:5em;
}
h2 {
font-size:3em;
}
body {
font-family:Georgia, serif;
}
Using a link element to include CSS with @font-face definitions is how some font hosting services recommend including their fonts. Google Fonts does this.
The server delivering the fonts does browser detection and delivers the CSS file with the appropriate font format.
Note that we are having using two Google Fonts -- Cabin Sketch and Cabin.
<link rel="stylesheet"
href="http://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Cabin+Sketch|Cabin"
type="text/css" />Our CSS:
h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6 {
font-family:"Cabin Sketch", sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size:3em;
}
h2 {
font-size:2em;
}
body {
font-family: Cabin, serif;
}
Note that nothing magical is going on here -- Google is simply returning CSS that uses @font-face with the font format appropriate for the browser making the request.
/* latin */
@font-face {
font-family: 'Cabin';
font-style: normal;
font-weight: 400;
src: local('Cabin Regular'), local('Cabin-Regular'), url(http://fonts.gstatic.com/s/cabin/v8/4VMQLG5UaE3m5rr_emmAqaCWcynf_cDxXwCLxiixG1c.woff2) format('woff2');
unicode-range: U+0000-00FF, U+0131, U+0152-0153, U+02C6, U+02DA, U+02DC, U+2000-206F, U+2074, U+20AC, U+2212, U+2215, U+E0FF, U+EFFD, U+F000;
}
/* latin */
@font-face {
font-family: 'Cabin Sketch';
font-style: normal;
font-weight: 400;
src: local('Cabin Sketch Regular'), local('CabinSketch-Regular'), url(http://fonts.gstatic.com/s/cabinsketch/v8/d9fijO34zQajqQvl3YHRCRampu5_7CjHW5spxoeN3Vs.woff2) format('woff2');
unicode-range: U+0000-00FF, U+0131, U+0152-0153, U+02C6, U+02DA, U+02DC, U+2000-206F, U+2074, U+20AC, U+2212, U+2215, U+E0FF, U+EFFD, U+F000;
}This is how some font hosting services have you include their fonts, including Adobe Edge Web Fonts.
The JavaScript does browser detection and then inserts the needed Markup/CSS into the page to include the fonts.
script element to include JavaScript:
<script src="//use.edgefonts.net/stencil-std.js"> </script>Our CSS:
h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6 {
font-weight:400;
font-family:"stencil-std", sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size:3em;
}
h2 {
font-size:2em;
}
body {
font-family: Georgia, serif;
}
Free
Licensed
Two approaches:
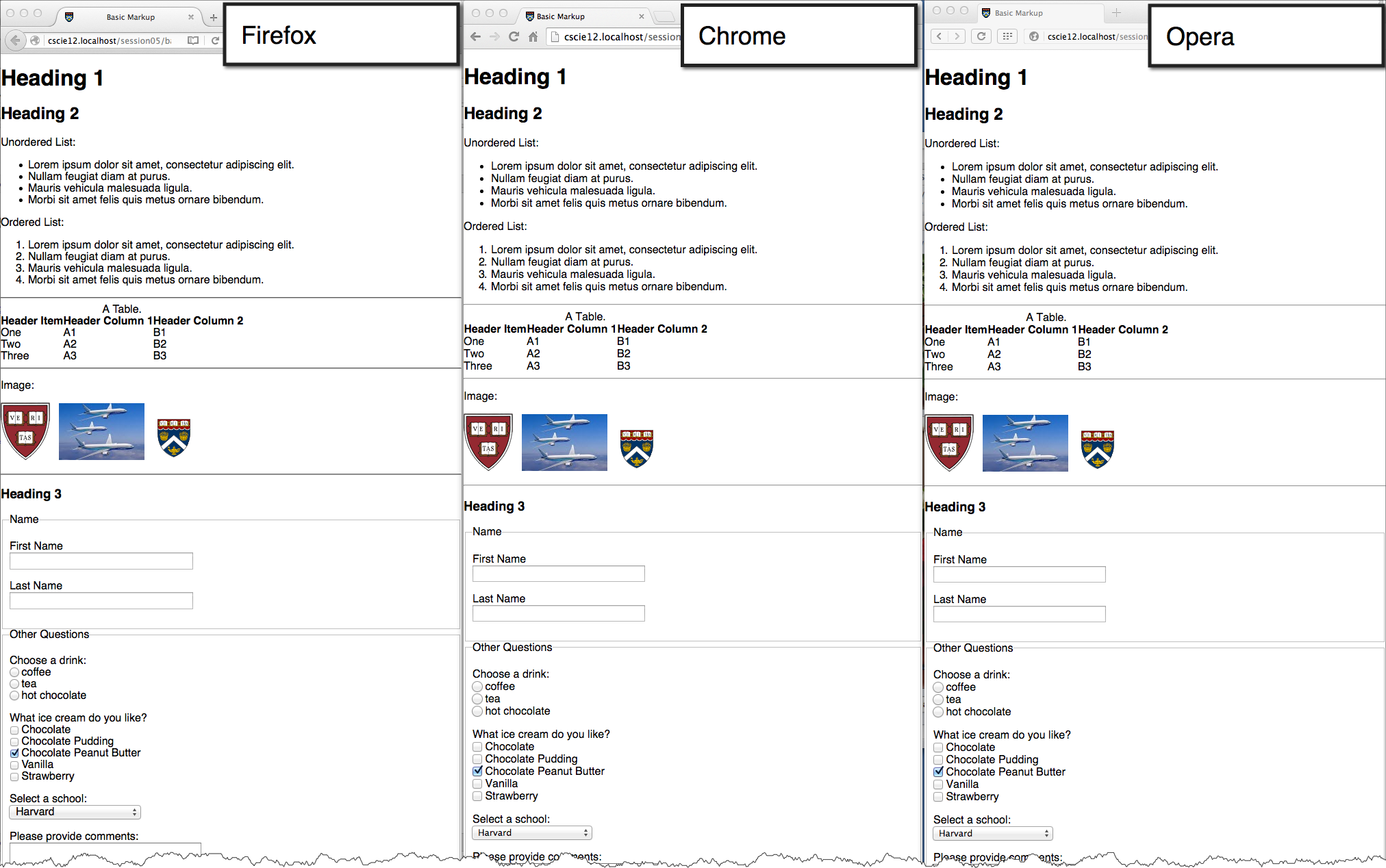
Sometimes it is useful to use a CSS stylesheet to "reset" styling for all elements. This attempts to start your styling with a "blank slate" instead of the browser defaults.
Basic Markup: | With CSS Reset: |
/* http://meyerweb.com/eric/tools/css/reset/
v2.0 | 20110126
License: none (public domain)
*/
html, body, div, span, applet, object, iframe,
h1, h2, h3, h4, h5, h6, p, blockquote, pre,
a, abbr, acronym, address, big, cite, code,
del, dfn, em, img, ins, kbd, q, s, samp,
small, strike, strong, sub, sup, tt, var,
b, u, i, center,
dl, dt, dd, ol, ul, li,
fieldset, form, label, legend,
table, caption, tbody, tfoot, thead, tr, th, td,
article, aside, canvas, details, embed,
figure, figcaption, footer, header, hgroup,
menu, nav, output, ruby, section, summary,
time, mark, audio, video {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
border: 0;
font-size: 100%;
font: inherit;
vertical-align: baseline;
}
/* HTML5 display-role reset for older browsers */
article, aside, details, figcaption, figure,
footer, header, hgroup, menu, nav, section {
display: block;
}
body {
line-height: 1;
}
ol, ul {
list-style: none;
}
blockquote, q {
quotes: none;
}
blockquote:before, blockquote:after,
q:before, q:after {
content: '';
content: none;
}
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
border-spacing: 0;
}
em units (relative to font-size)Define region widths based upon fixed sizes (pixels).
Use "div" elements to define areas and CSS to arrange them on the page.
<div id="wrapper">
<div id="header"> ... </div>
<div id="maincontent">
...
</div>
<div id="navigation">
...
</div>
<div id="footer"> ... </div>
</div>
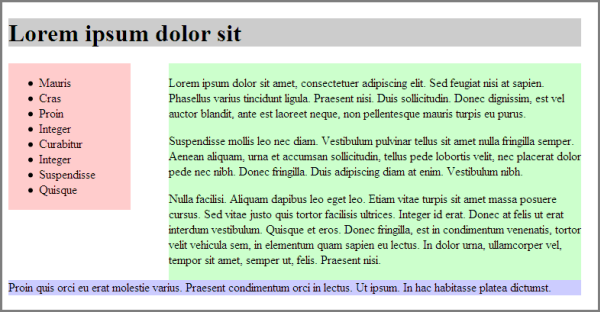
<div id="wrapper"><div id="header"><h1>Lorem ipsum dolor sit</h1></div><div id="maincontent"><p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Sed feugiat nisi at sapien. Phasellus varius tincidunt ligula. Praesent nisi. Duis sollicitudin. Donec dignissim, est vel auctor blandit, ante est laoreet neque, non pellentesque mauris turpis eu purus.</p>
<p>Suspendisse mollis leo nec diam. Vestibulum pulvinar tellus sit amet nulla fringilla semper. Aenean aliquam, urna et accumsan sollicitudin, tellus pede lobortis velit, nec placerat dolor pede nec nibh. Donec fringilla. Duis adipiscing diam at enim. Vestibulum nibh.</p>
<p>Nulla facilisi. Aliquam dapibus leo eget leo. Etiam vitae turpis sit amet massa posuere cursus. Sed vitae justo quis tortor facilisis ultrices. Integer id erat. Donec at felis ut erat interdum vestibulum. Quisque et eros. Donec fringilla, est in condimentum venenatis, tortor velit vehicula sem, in elementum quam sapien eu lectus. In dolor urna, ullamcorper vel, tempor sit amet, semper ut, felis. Praesent nisi.</p>
</div><div id="navigation"><ul>
<li>Mauris</li>
<li>Cras</li>
<li>Proin</li>
<li>Integer</li>
<li>Curabitur</li>
<li>Integer</li>
<li>Suspendisse</li>
<li>Quisque</li>
</ul></div><div id="footer">Proin quis orci eu erat molestie varius. Praesent condimentum orci in lectus. Ut ipsum. In hac habitasse platea dictumst.</div></div> In style
element
(<style type="text/css">) within head element:
#wrapper {
width: 750px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
#header {
width: 100%;
background-color: #ccc;
}
#footer {
clear: both;
background-color: #ccf;
}
#navigation {
width: 160px;
float: left;
background-color: #fcc;
}
#maincontent {
width: 540px;
float: right;
background-color: #cfc;
} Define region width based on percentages (relative to browser window width).
<div id="wrapper">
<div id="header"> ... </div>
<div id="maincontent">
...
</div>
<div id="navigation">
...
</div>
<div id="footer"> ... </div>
</div>
<div id="wrapper"><div id="header"><h1>Lorem ipsum dolor sit</h1></div><div id="maincontent"><p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Sed feugiat nisi at sapien. Phasellus varius tincidunt ligula. Praesent nisi. Duis sollicitudin. Donec dignissim, est vel auctor blandit, ante est laoreet neque, non pellentesque mauris turpis eu purus.</p>
<p>Suspendisse mollis leo nec diam. Vestibulum pulvinar tellus sit amet nulla fringilla semper. Aenean aliquam, urna et accumsan sollicitudin, tellus pede lobortis velit, nec placerat dolor pede nec nibh. Donec fringilla. Duis adipiscing diam at enim. Vestibulum nibh.</p>
<p>Nulla facilisi. Aliquam dapibus leo eget leo. Etiam vitae turpis sit amet massa posuere cursus. Sed vitae justo quis tortor facilisis ultrices. Integer id erat. Donec at felis ut erat interdum vestibulum. Quisque et eros. Donec fringilla, est in condimentum venenatis, tortor velit vehicula sem, in elementum quam sapien eu lectus. In dolor urna, ullamcorper vel, tempor sit amet, semper ut, felis. Praesent nisi.</p>
</div><div id="navigation"><ul>
<li>Mauris</li>
<li>Cras</li>
<li>Proin</li>
<li>Integer</li>
<li>Curabitur</li>
<li>Integer</li>
<li>Suspendisse</li>
<li>Quisque</li>
</ul></div><div id="footer">Proin quis orci eu erat molestie varius. Praesent condimentum orci in lectus. Ut ipsum. In hac habitasse platea dictumst.</div></div> In style
element
(<style type="text/css">) within head element:
#wrapper {
width: 90%;
margin: 0 auto;
}
#header {
width: 100%;
background-color: #ccc;
}
#footer {
clear: both;
background-color: #ccf;
}
#navigation {
width: 30%;
float: left;
background-color: #fcc;
}
#maincontent {
width: 70%;
float: right;
background-color: #cfc;
} Define region widths (and margin and padding) in "em" units (relative to font size).

<div id="wrapper"><div id="header"><h1>Lorem ipsum dolor sit</h1></div><div id="maincontent"><p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Sed feugiat nisi at sapien. Phasellus varius tincidunt ligula. Praesent nisi. Duis sollicitudin. Donec dignissim, est vel auctor blandit, ante est laoreet neque, non pellentesque mauris turpis eu purus.</p>
<p>Suspendisse mollis leo nec diam. Vestibulum pulvinar tellus sit amet nulla fringilla semper. Aenean aliquam, urna et accumsan sollicitudin, tellus pede lobortis velit, nec placerat dolor pede nec nibh. Donec fringilla. Duis adipiscing diam at enim. Vestibulum nibh.</p>
<p>Nulla facilisi. Aliquam dapibus leo eget leo. Etiam vitae turpis sit amet massa posuere cursus. Sed vitae justo quis tortor facilisis ultrices. Integer id erat. Donec at felis ut erat interdum vestibulum. Quisque et eros. Donec fringilla, est in condimentum venenatis, tortor velit vehicula sem, in elementum quam sapien eu lectus. In dolor urna, ullamcorper vel, tempor sit amet, semper ut, felis. Praesent nisi.</p>
</div><div id="navigation"><ul>
<li>Mauris</li>
<li>Cras</li>
<li>Proin</li>
<li>Integer</li>
<li>Curabitur</li>
<li>Integer</li>
<li>Suspendisse</li>
<li>Quisque</li>
</ul></div><div id="footer">Proin quis orci eu erat molestie varius. Praesent condimentum orci in lectus. Ut ipsum. In hac habitasse platea dictumst.</div></div> In style
element
(<style type="text/css">) within head element:
body {
font-family: Lucida Grande, Verdana, serif;
}
#wrapper {
width: 45em;
margin: 0 auto;
border: medium solid black;
}
#header {
width: 44em;
padding: 0.5em;
background-color: #ccc;
}
#footer {
width: 44em;
padding: 0.5em;
clear: both;
background-color: #ccf;
}
#navigation {
width: 13em;
padding: 0.5em;
float: left;
background-color: #fcc;
}
#maincontent {
width: 30em;
padding: 0.5em;
float: right;
background-color: #cfc;
} header, footer, navigation, primary content, secondary content

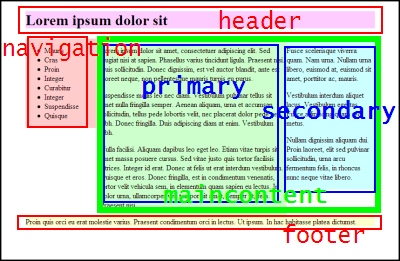
<div id="wrapper"><div id="header"><h1>Lorem ipsum dolor sit</h1></div><div id="maincontent"><div id="primary"><p>Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetuer adipiscing elit. Sed feugiat nisi at sapien. Phasellus varius tincidunt ligula. Praesent nisi. Duis sollicitudin. Donec dignissim, est vel auctor blandit, ante est laoreet neque, non pellentesque mauris turpis eu purus.</p>
<p>Suspendisse mollis leo nec diam. Vestibulum pulvinar tellus sit amet nulla fringilla semper. Aenean aliquam, urna et accumsan sollicitudin, tellus pede lobortis velit, nec placerat dolor pede nec nibh. Donec fringilla. Duis adipiscing diam at enim. Vestibulum nibh.</p>
<p>Nulla facilisi. Aliquam dapibus leo eget leo. Etiam vitae turpis sit amet massa posuere cursus. Sed vitae justo quis tortor facilisis ultrices. Integer id erat. Donec at felis ut erat interdum vestibulum. Quisque et eros. Donec fringilla, est in condimentum venenatis, tortor velit vehicula sem, in elementum quam sapien eu lectus. In dolor urna, ullamcorper vel, tempor sit amet, semper ut, felis. Praesent nisi.</p>
</div><div id="secondary"><p>Fusce scelerisque viverra quam. Nam urna. Nullam urna libero, euismod at, euismod sit amet, porttitor ac, mauris.</p>
<p>Vestibulum interdum aliquet lacus. Vestibulum egestas. Fusce adipiscing quam sed metus.</p>
<p>Nullam dignissim aliquam dui. Proin laoreet, elit sed pulvinar sollicitudin, urna arcu fermentum felis, in rhoncus nunc neque vitae libero.</p>
</div></div><div id="navigation"><ul>
<li>Mauris</li>
<li>Cras</li>
<li>Proin</li>
<li>Integer</li>
<li>Curabitur</li>
<li>Integer</li>
<li>Suspendisse</li>
<li>Quisque</li>
</ul></div><div id="footer">Proin quis orci eu erat molestie varius. Praesent condimentum orci in lectus. Ut ipsum. In hac habitasse platea dictumst.</div></div> In style
element
(<style type="text/css">) within head element:
#wrapper {
width: 750px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
#header {
width: 100%;
background-color: #fcf;
}
#footer {
clear: both;
background-color: #ffc;
}
#navigation {
width: 160px;
float: left;
background-color: #fcc;
}
#maincontent {
width: 590px;
float: right;
}
#primary {
width: 400px;
float: left;
background-color: #cfc;
}
#secondary {
width: 190px;
float: right;
background-color: #cff;
}Site is "responsive" to different devices.

CSS media query:
/* Larger than mobile */
@media (min-width: 400px) { /* specific rules go here */ }
/* Larger than phablet (also point when grid becomes active) */
@media (min-width: 550px) { /* specific rules go here */ }
/* Larger than tablet */
@media (min-width: 750px) { /* specific rules go here */ }
/* Larger than desktop */
@media (min-width: 1000px) { /* specific rules go here */ }
/* Larger than Desktop HD */
@media (min-width: 1200px) { /* specific rules go here */ }Media queries can be used to include style sheets (media attribute) or in CSS rules (@media rule) or @import statement
Link to stylesheet
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css"
media="screen and (max-device-width: 480px)"
href="smallscreen.css" />CSS rule
@media screen and (max-device-width: 480px) {
/* rules for small screens */
.column { float: none; }
}@import statement
@import url('smallscreen.css') screen and (max-device-width: 480px);


 The Little Book of HTML/CSS Frameworks,
The Little Book of HTML/CSS Frameworks,
PDF - The Little Book of HTML/CSS Frameworks
Copyright © David Heitmeyer